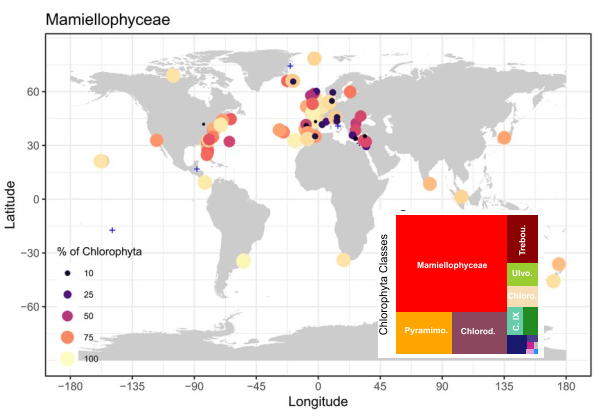
 Mamiellophyceae dominate green algae in coastal waters
Mamiellophyceae dominate green algae in coastal waters
Green microalgae in marine coastal waters : The Ocean Sampling Day (OSD) dataset
Abstract
The ecology and distribution of green phytoplankton (Chlorophyta) in the ocean is poorly known because most studies have focused on groups with large cell size such as diatoms or dinoflagellates that are easily recognized by traditional techniques such as microscopy. The Ocean Sampling Day (OSD) project sampled surface waters quasi-simultaneously at 141 marine locations, mostly in coastal waters. The analysis of the 18S V4 region OSD metabarcoding dataset reveals that Chlorophyta are ubiquitous and can be locally dominant in coastal waters. Chlorophyta represented 29% of the global photosynthetic reads (Dinoflagellates excluded) and their contribution was especially high at oligotrophic stations (up to 94%) and along the European Atlantic coast. Mamiellophyceae dominated most coastal stations. At some coastal stations, they were replaced by Chlorodendrophyceae, Ulvophyceae, Trebouxiophyceae or Chlorophyceae as the dominating group, while oligotrophic stations were dominated either by Chloropicophyceae or the uncultured prasinophytes clade IX. Several Chlorophyta classes showed preferences in terms of nitrate concentration, distance to the coast, temperature and salinity. For example, Chlorophyceae preferred cold and low salinity coastal waters, and prasinophytes clade IX warm, high salinity, oligotrophic oceanic waters