BIOS5316
Daniel Vaulot
2023-10-05

Culture information management
Outline
- The Roscoff Culture Collection
- Strain information: metadata
- Keeping track of the metadata: database
- Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS)
Station Biologique de Roscoff
Station Biologique de Roscoff
- 1872 - Antoine Lacaze-Duthiers (150 years ago)
- CNRS and Sorbonne Université
- Staff: 350
- Students : 1,000-2,000 per year


Ecologie of Marine Plankton team (ECOMAP)
- Scientists: 10
- Staff: ~ 40
- Research themes:
- Viruses
- Bacteria
- Cyanobacteria
- Symbioses
- Parasitism

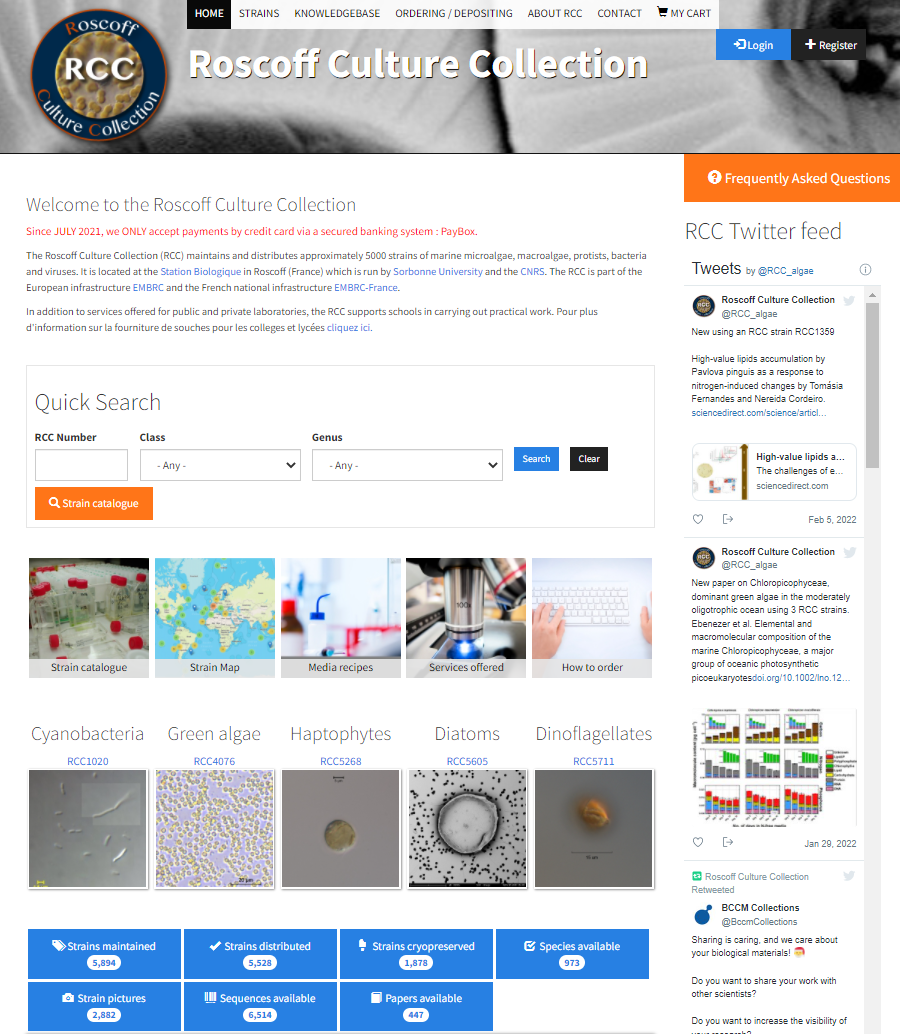
Roscoff Culture Collection
- Created 1998
- One of the largest marine algal collection
- 5,000 strains distributed
- https://roscoff-culture-collection.org/
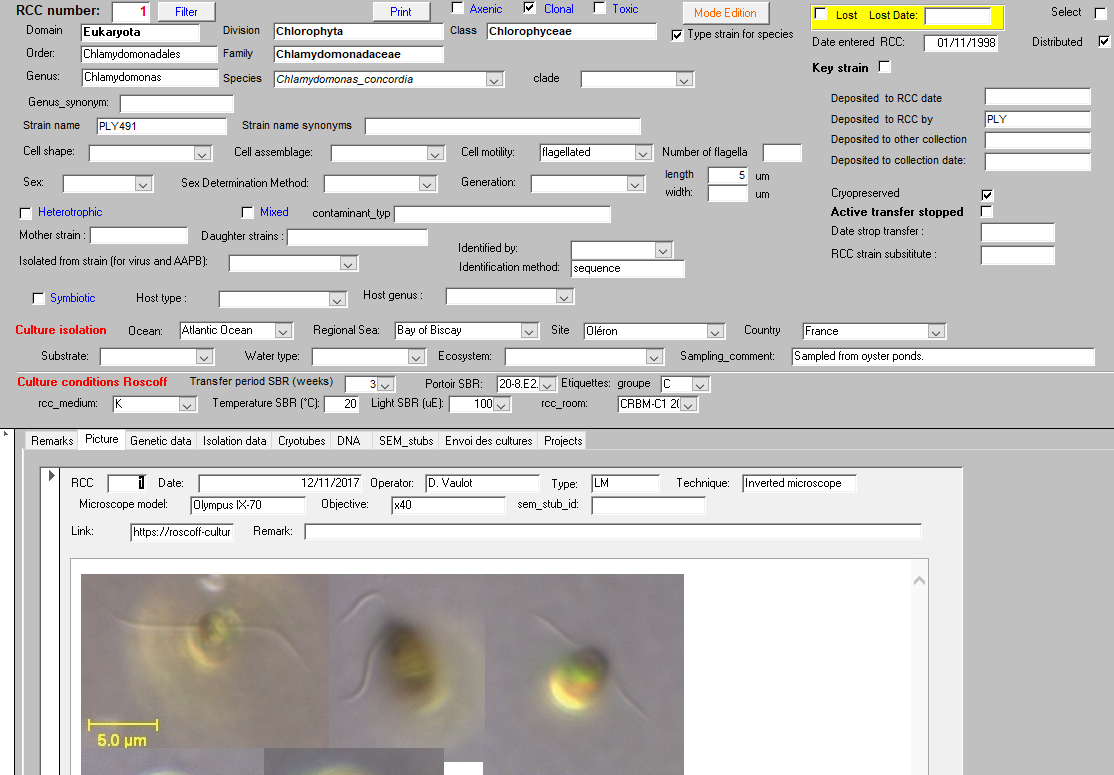
Metadata
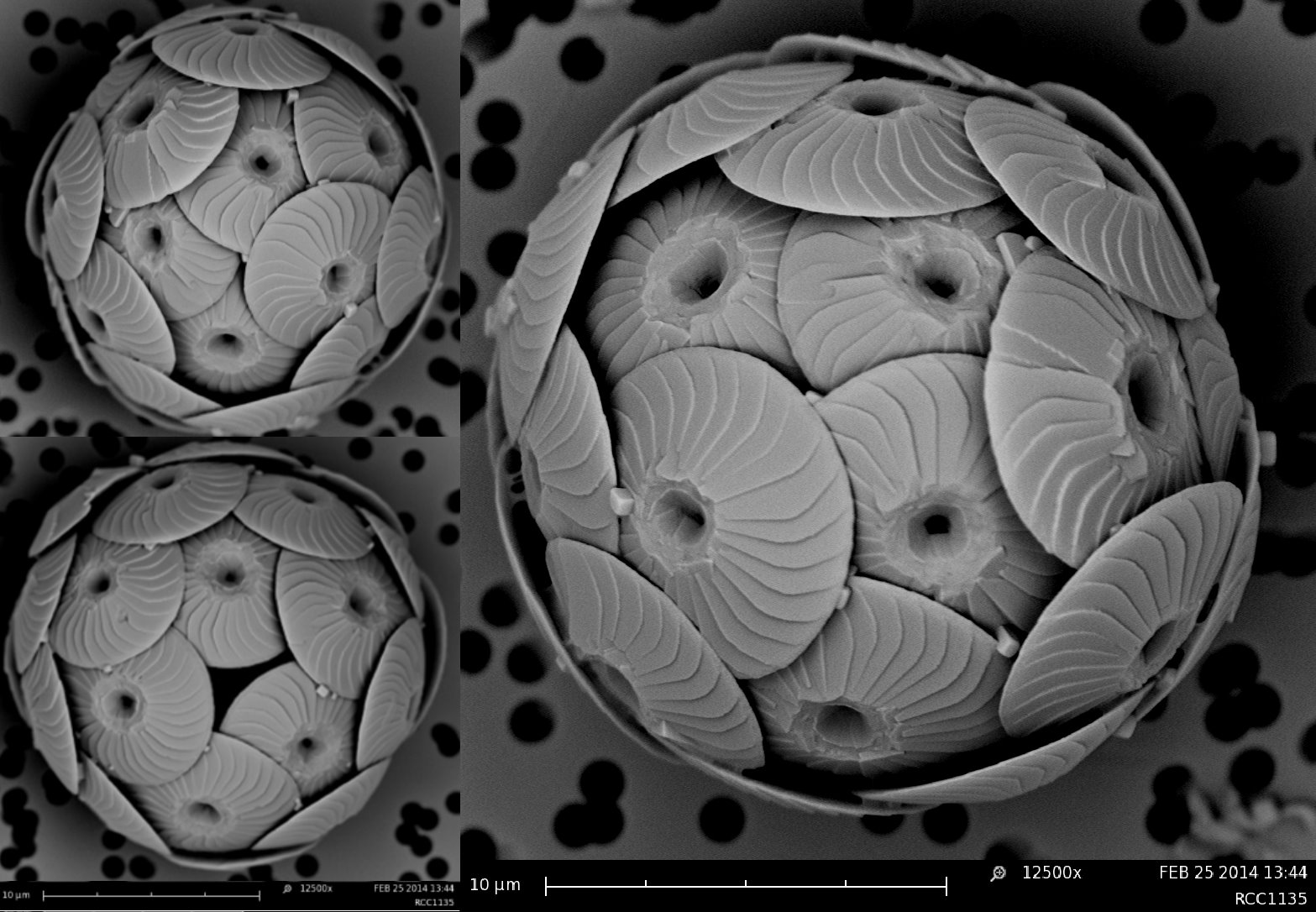
What are metadata ?
Metadata are data related to each strain.
They are used to determine the ID-card of the strain.
- Unique identifier
- Strain name
- Taxonomy
- Origin
- Status of strain
- Images
- Maintenance conditions
- ABS status
- Sequences
- Publications
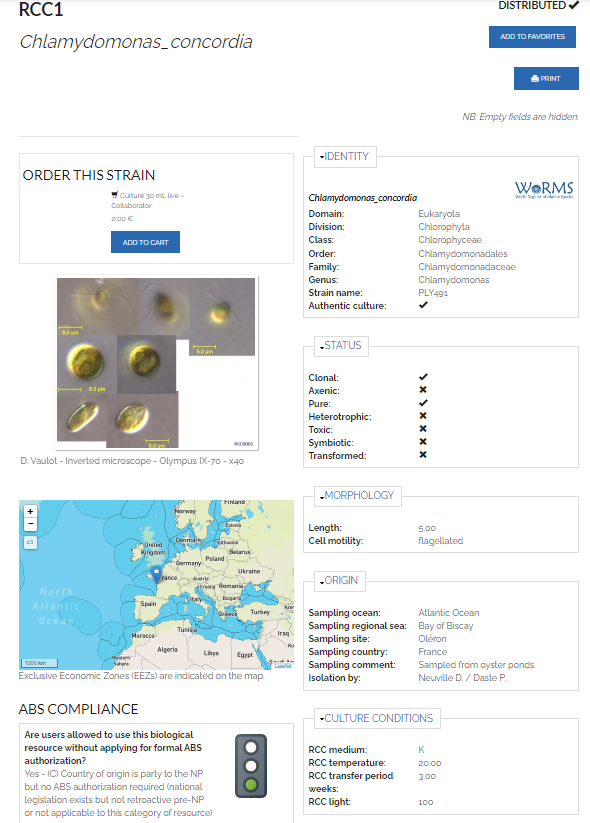
Strain identification
- Unique identifier (RCC1, RCC2…)
- This number is fixed and should be always used
- It is given only for stable cultures
- Strain name
- This is given during the isolation process
- It contains reference to cruise or project
- Important to provide synomyms if they exists

Strain identification
- Taxonomy
- Follow standard (Algaebase)
- Be consistent
- Can be in separate table (see later)
- RCC use 7 levels
- Domain
- Division
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
- Identification can be at higher level only (e.g. class)

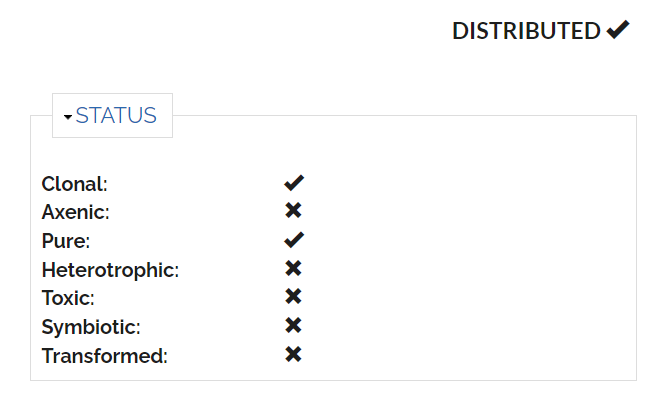
Strain status
- Alive ?
- Never erase information about a strain even if it has been lost.
- Lost: Yes/no
- Date of loss
- Distributed ?
- Strains may be kept private until described
- Clonal ?
- Arise from single cells
- Mixed ?
- With heterotroph ?
- ABS status (Nagoya convention)
Strain isolation
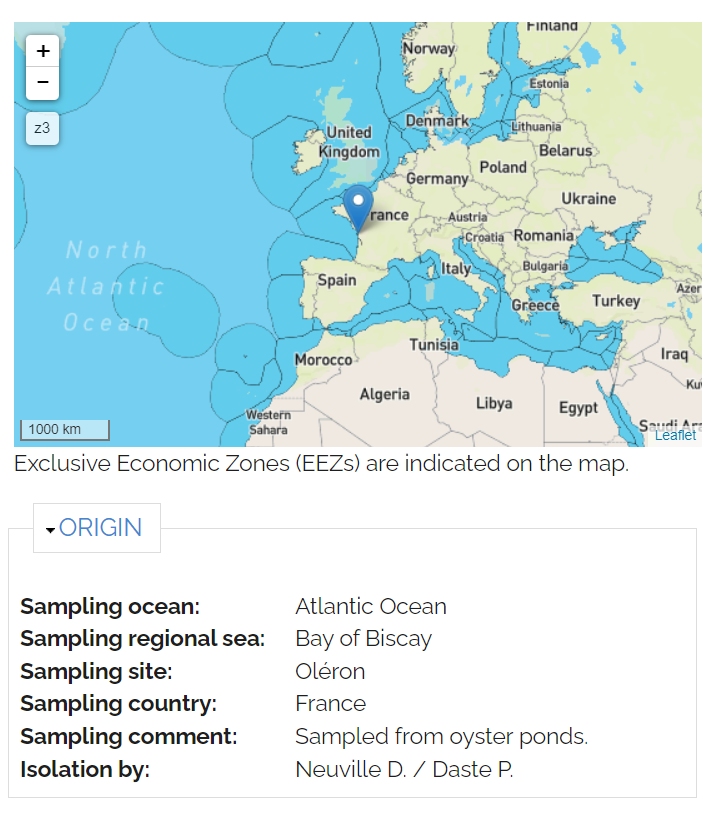
- Sampling
- Date (see ABS)
- Position
- Depth
- Ocean / Regional Sea
- Site
- Country (see ABS)
- Substrate (water, sediment)
- Temperature / Salinity
- Isolation
- Method
- Medium
- Temperature
- Light
Phenotype
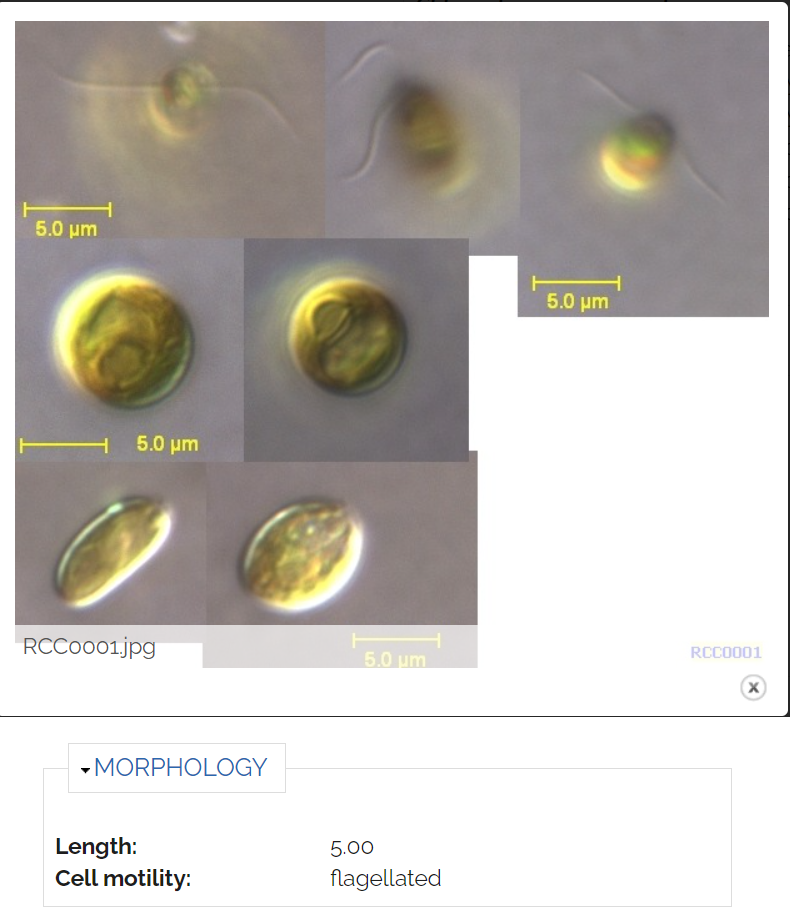
- Life mode
- Phototrophic / Heterotrophic
- Symbiotic
- Morphology
- Cell size
- Cell shape
- Motility
- Colonial ?
- Images
Other information
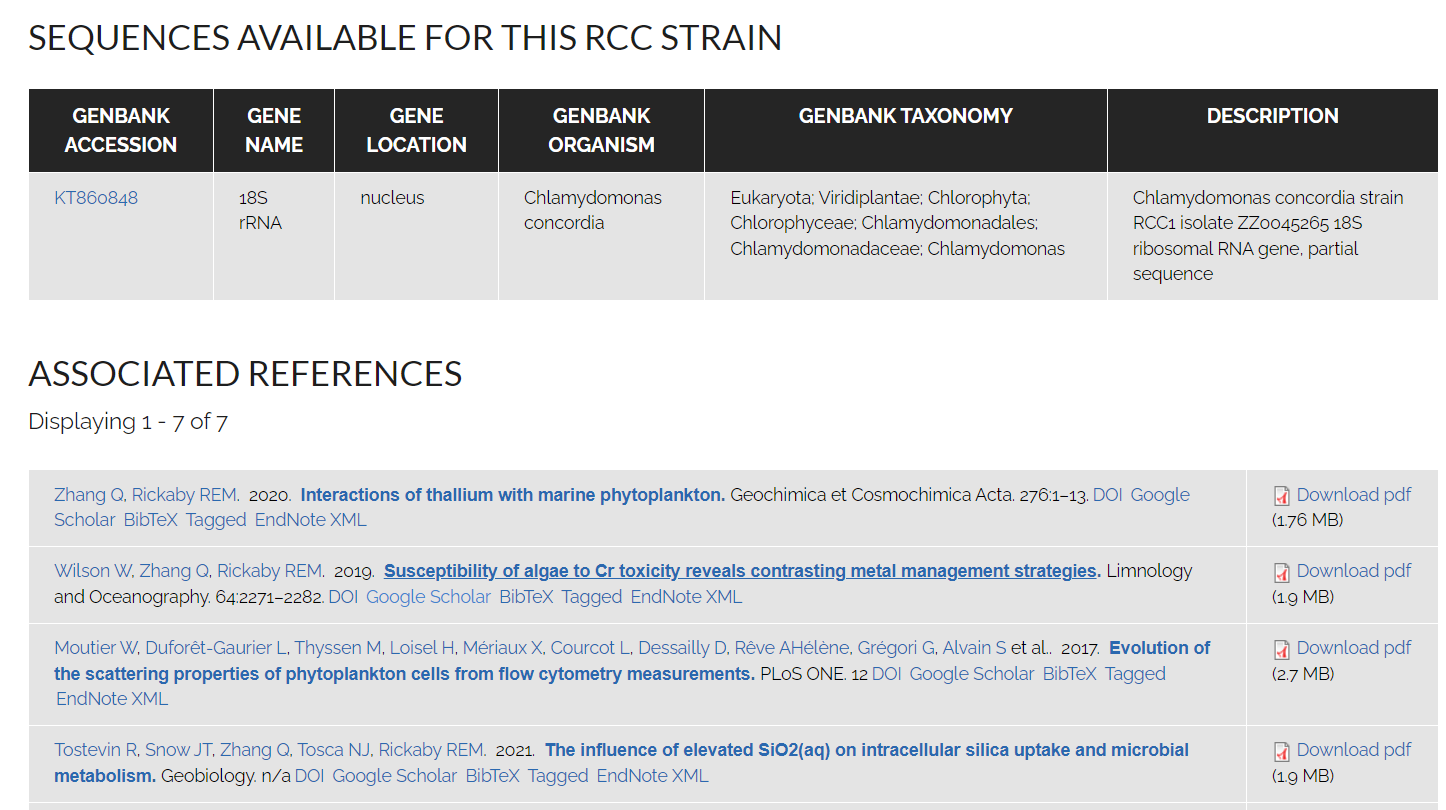
- Genetic sequences
- Pigment composition
- References for the strain
Management
- Culture localisation
- Media batches
- Cryoconservation
- DNA
- Distribution
Databases
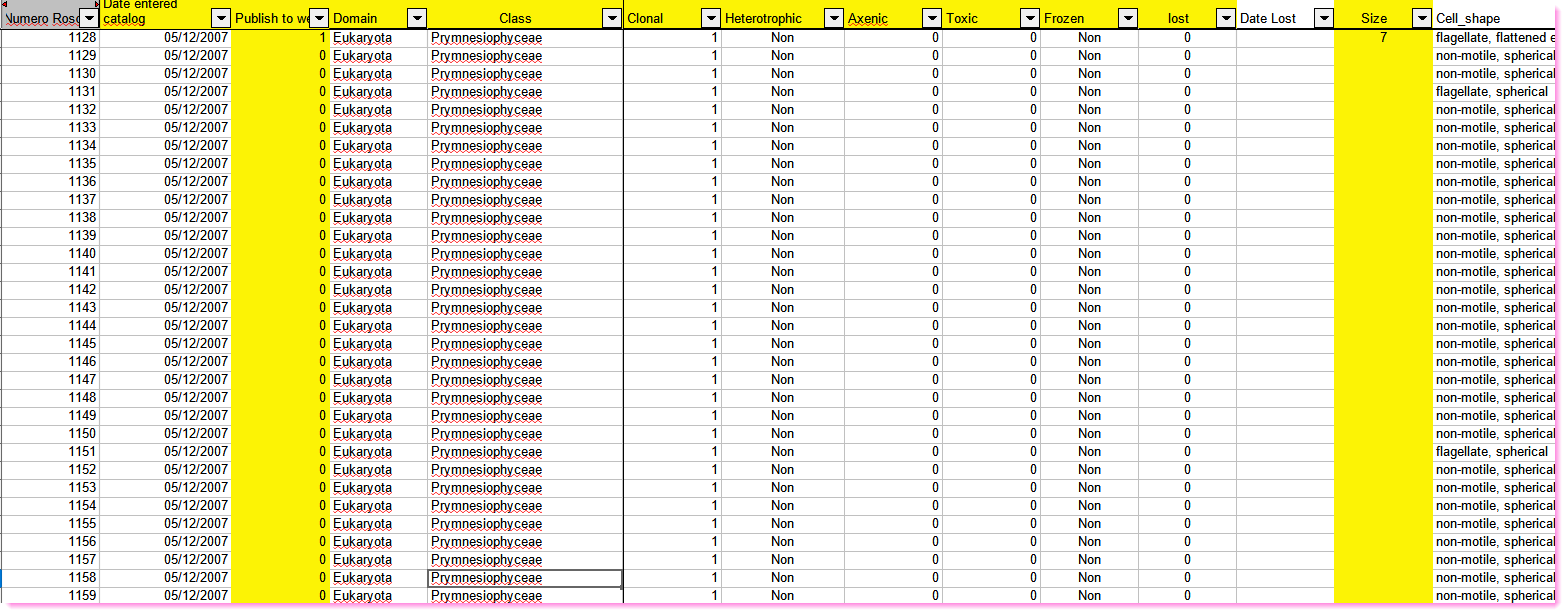
How to keep track of the information ?
Excel worksheet
Advantages
- Everyone can use Excel
Disadvantages
- Difficult to share
- No rule enforcement for each field
- Too many formatting
Google worksheet
Advantages
- More easy to share
- Can trace who modifies
Disadvantages
- Same as Excel
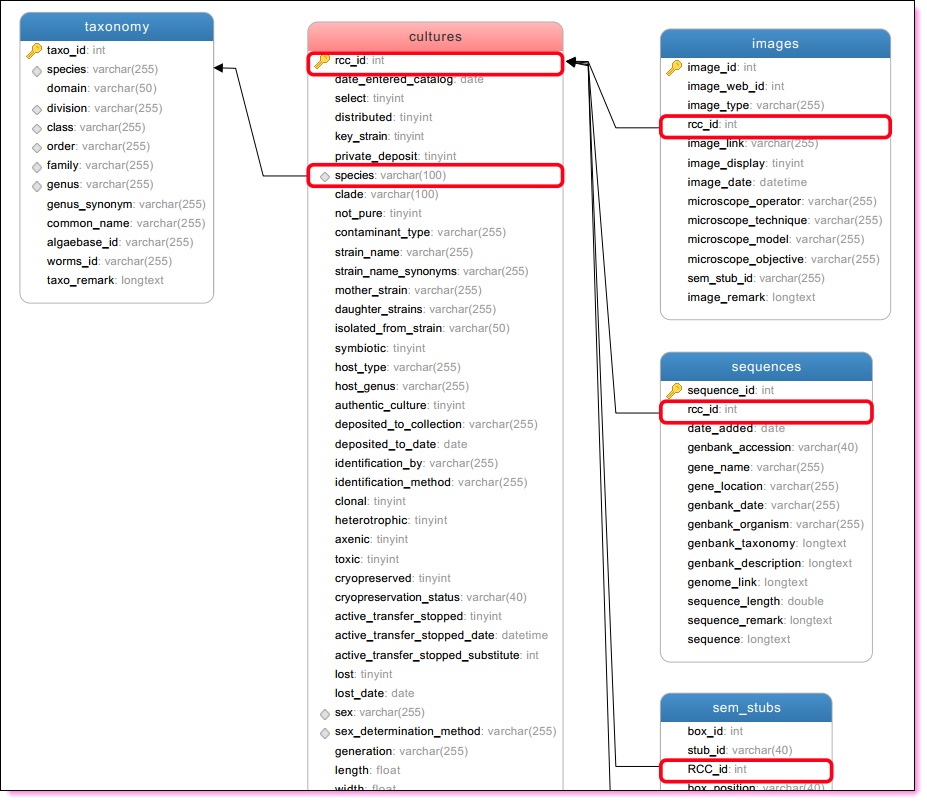
How to keep track of the information ?
SQL relational databases
Advantages
- Allow to structure information much better
- Relationships between different tables
- Many choices for implementation:
- local (SQlite or Access)
- remote on the cloud (MySQL)
Disadvantages
- Requires using specific tools
- Need computer skills
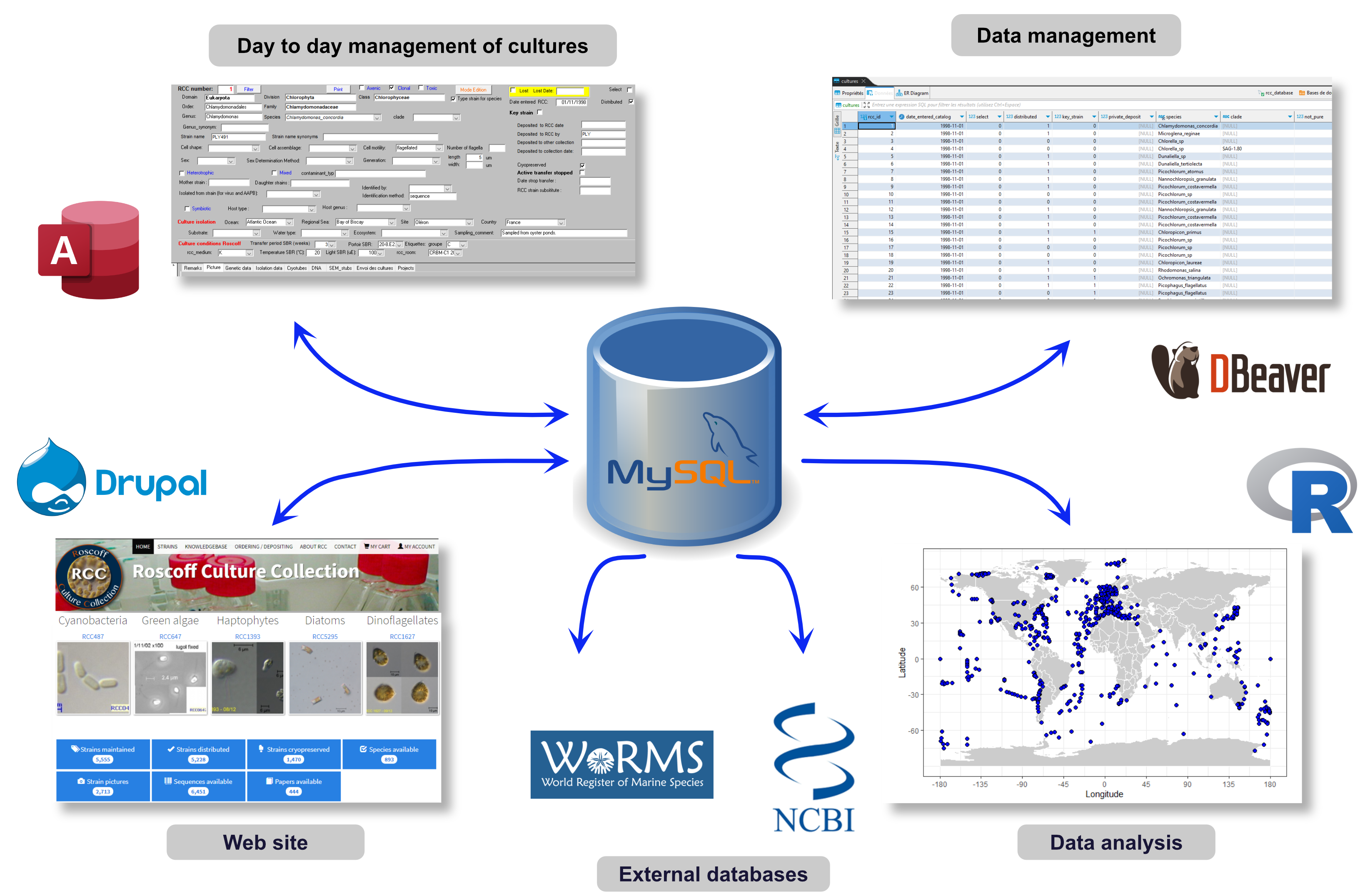
The Roscoff Culture Collection solution
This solution has been elaborated over 20 years with many iterations…
- Start from a database
- Initially Microsoft Access
- Since 2017 MySQL
- Link to web site
- 3 generations
Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS)
Legal vs Practice

Legal framework

Using biological resources
- Sampling/Acquisition - ABS
- Housing
- Utilization - ABS
Best practice
- OECD Best Practice Guidelines for Biological Resource Centres (2007)
- ISO 9001 : Quality Management System
- ISO 20387:2018 : General requirements for biobanking (based on French NF S96-900 standard)

ABS: long journey
- Before Convention on Biological Diversity (Rio 1992): Biodiversity (animals, plants, microorganisms) considered as common heritage of mankind
- After CBD (1992): Adoption of concept that states have sovereign rights over their biological resources
- 2010: Adoption of Nagoya Protocol (NP) to CBD: sets out core obligations for its contracting Parties to take measures in relation to access to genetic resources, benefit-sharing and compliance.
- 2014: European ABS Directive 511-2014 defines responsibilities of Member States for enforcing compliance to NP
- From 2014: national laws (or not…)
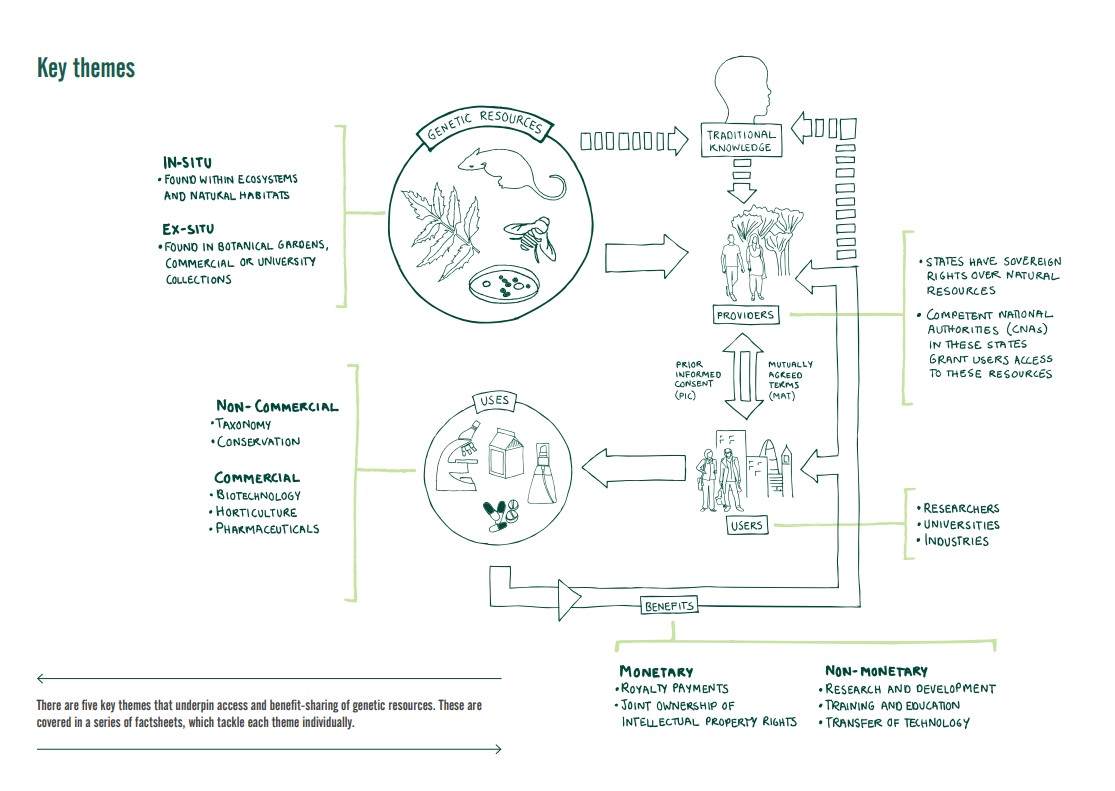
Nagoya protocol - 1990

United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) - 1994
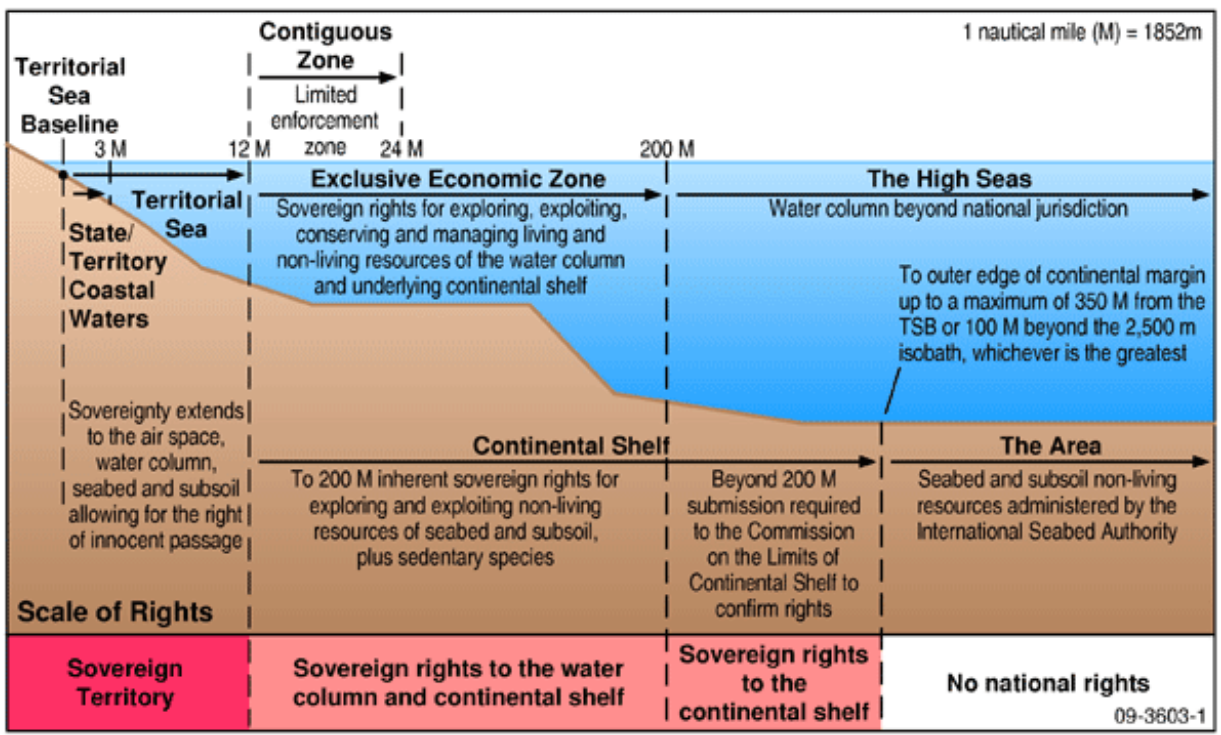
Important points
- Unique identifier for each strain
- Never delete information (e.g. lost strains)
- Sampling information is critical for ABS