R course
Daniel Vaulot
2023-01-26



Metabarcode analysis - Introduction
Outline
Metabarcoding data
Factors affecting protist communities
Diversity
Intro to Metabarcoding
Metabarcoding
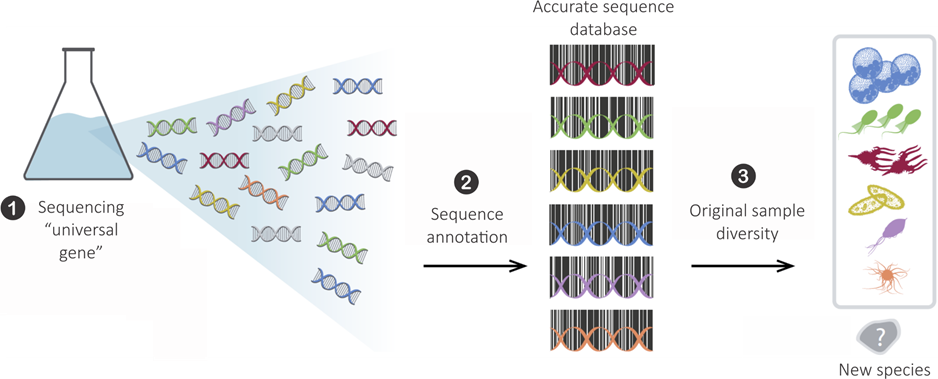
Sequences
Fastq files

Cluster
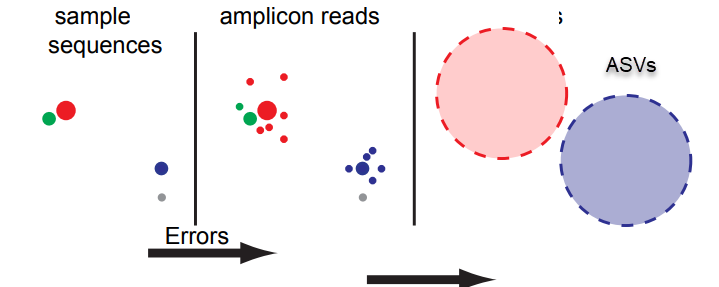
Assign
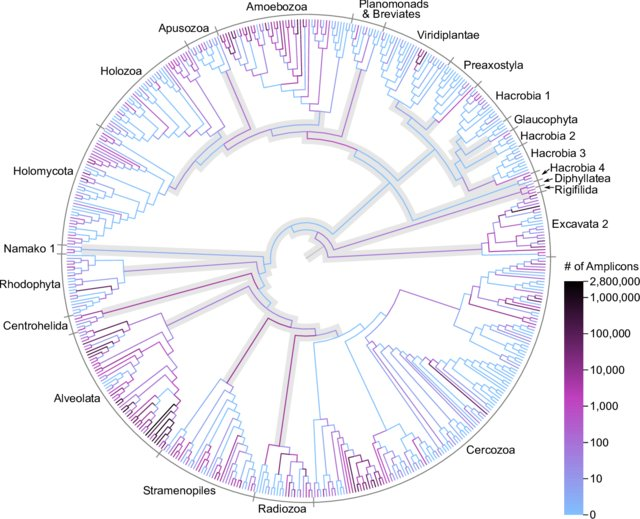
Metabarcoding pipeline
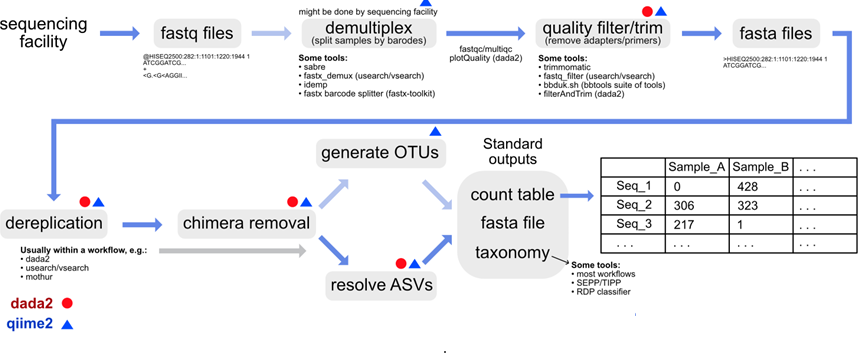
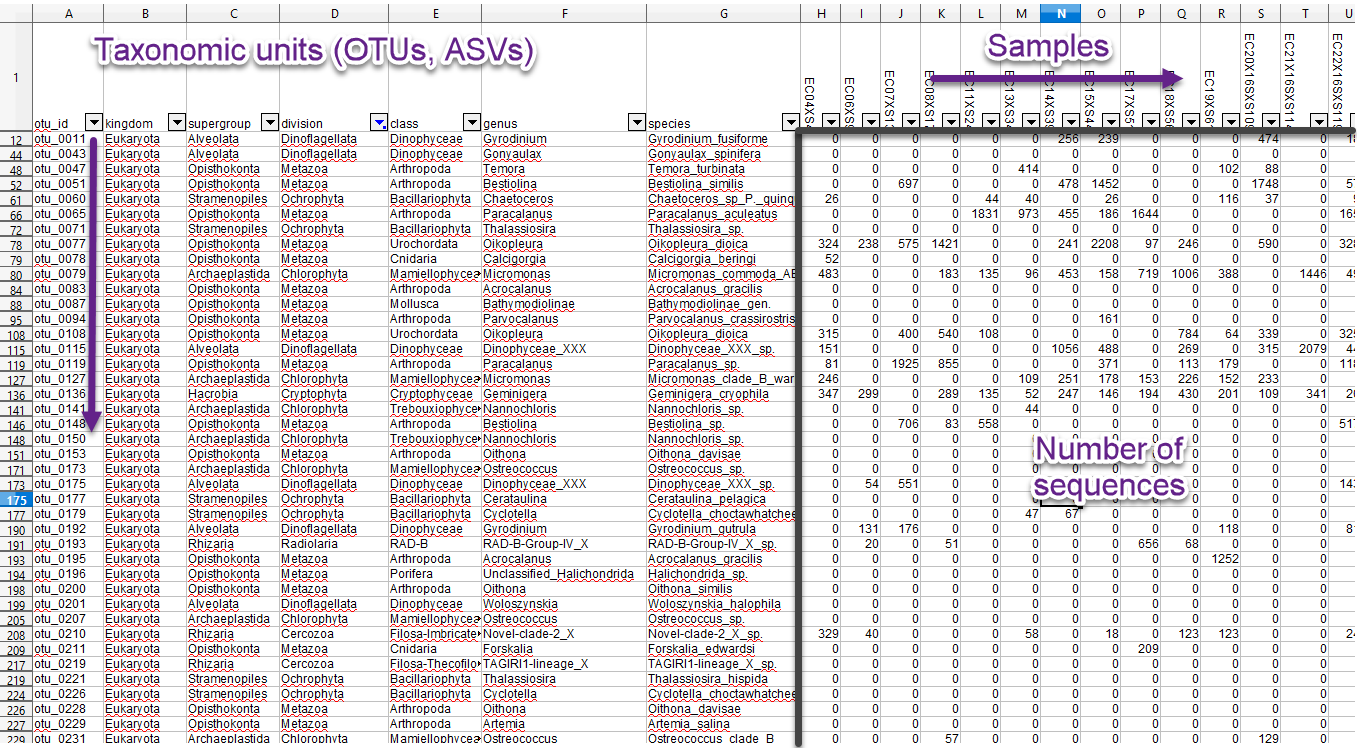
Data tables - ASVs
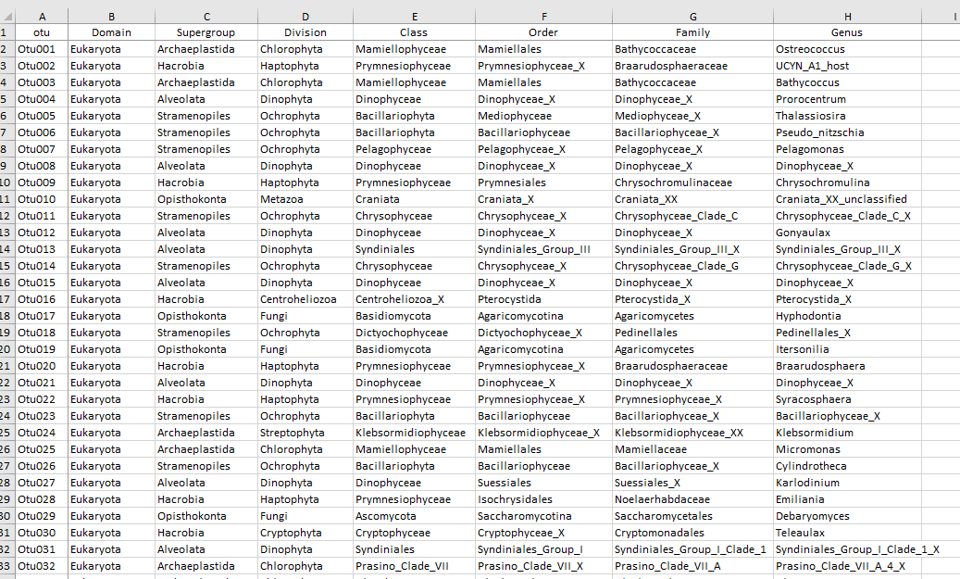
Data tables - Abundance
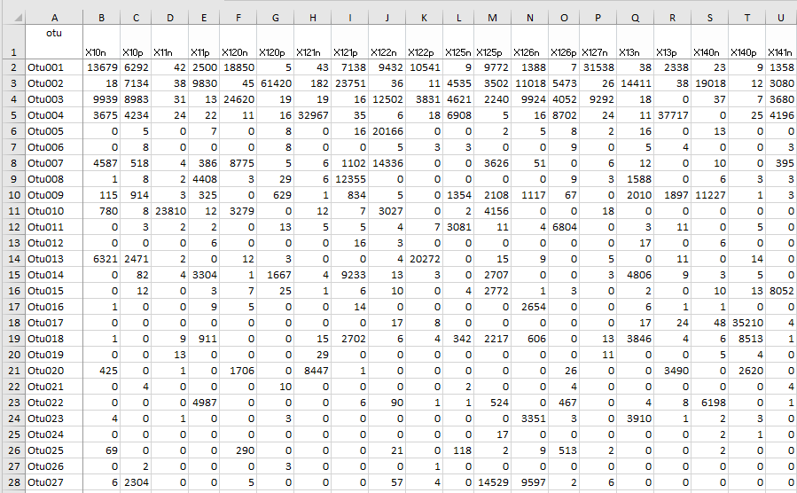
Data tables - Metadata
Data tables - Merged
Factors affecting protist communities
Substrate
- Water
- Ice
- Sediment
- Soil
- Microbiome
Ecosystem
- Oceanic
- Coastal
- Rivers
- Lakes
- Terrestrial
Size fraction
- Total (0.2 µm -> 100 µm)
- Pico (0.2 µm -> 2-3 µm)
- Nano (2-3 µm -> 20 µm)
- Micro (20 µm -> 100-200 µm)
- Meso (100 µm -> 1000 µm)
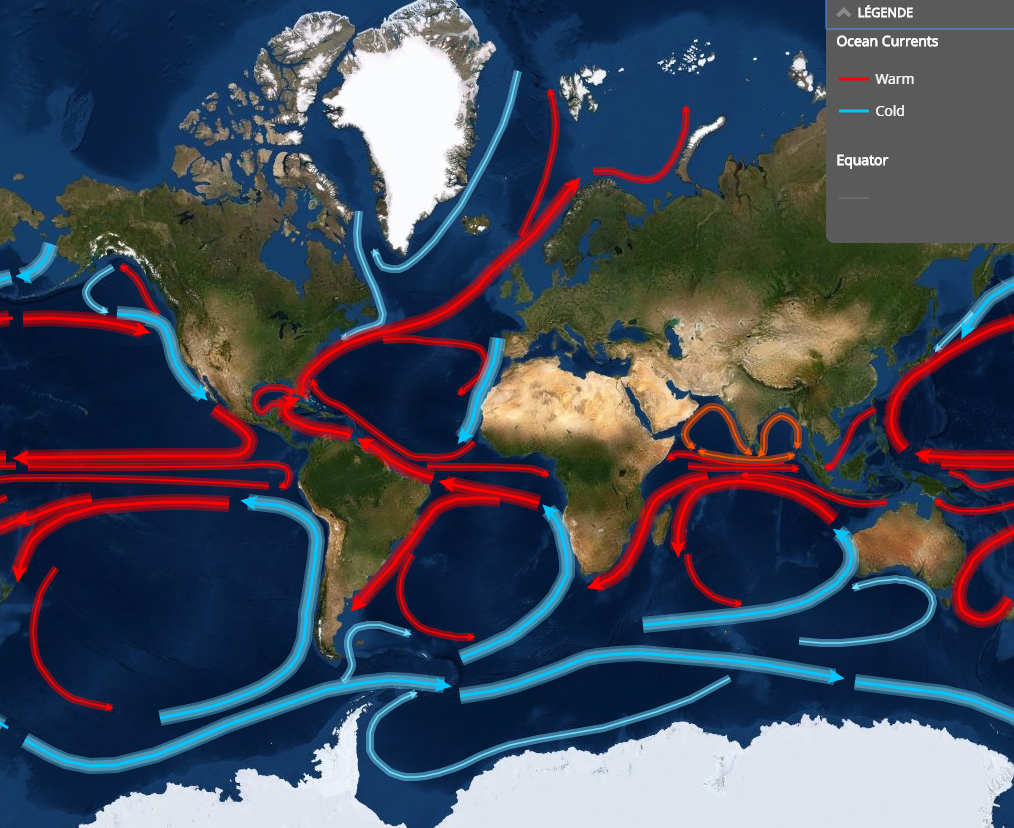
Factors affecting protist communities
Environmental conditions
In oceanic waters:
- temperature
- salinity
- light
- nutrients
… which depend on:
- substrate (water vs.ice)
- latitude
- time of the year
- depth
- oceanic currents
- proximity of coast
Estimating diversity
Diversity
Microbial species in a sample
- species richness: total number of species
- species abundance: proportion of each species
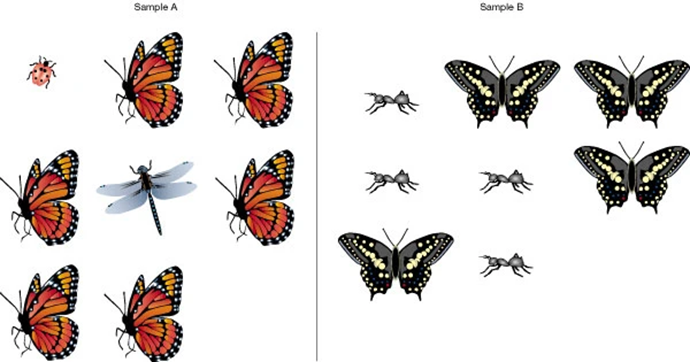
Richness vs. Evenness
Diversity
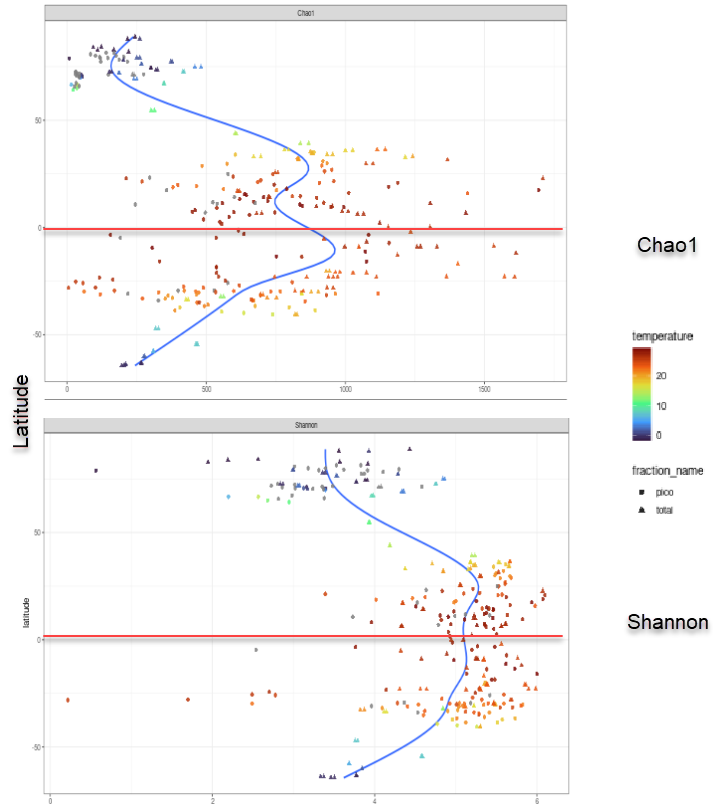
Alpha diversity - Diversity within a given sample
- Chao 1 is a non-parametric estimator of the number of species in a community.
- Shannon index1
\(H = - \sum_{i=1}^{S} p_i \cdot \log{p_i}\)
Where:
\(p_i\) = fraction of the entire population made up of species \(i\) (proportion of a species i relative to total number of species present)
\(S\) = numbers of species encountered
A high value of \(H\) would be a representative of a diverse and equally distributed community and lower values represent less diverse community. A value of 0 would represent a community with just one species.
Diversity
Alpha diversity - Effect of latitude
Diversity
Beta diversity - Compare diversity between samples
Compute distance between samples:
Bray-Curtis dissimilarity: use abundance information
- Varies between 0 and 1:
- 0 means the two samples have the same composition
- 1 means the two samples do not share any species
\(BC_{jk} = 1 - \frac{2\sum_{i=1}^{p}min(N_{ij},N_{ik})}{\sum_{i=1}^{p}(N_{ij} + N_{ik})}\)
where \(N_{ij}\) is the abundance of species \(i\) in sample \(j\) and \(p\) the total number of species
Jaccard similarity index
- Number of common species between samples divided by total number of species in the two samples \(J(A,B) = \frac{|A \cap B|}{|A \cup B|}\)
- Ordinate the samples
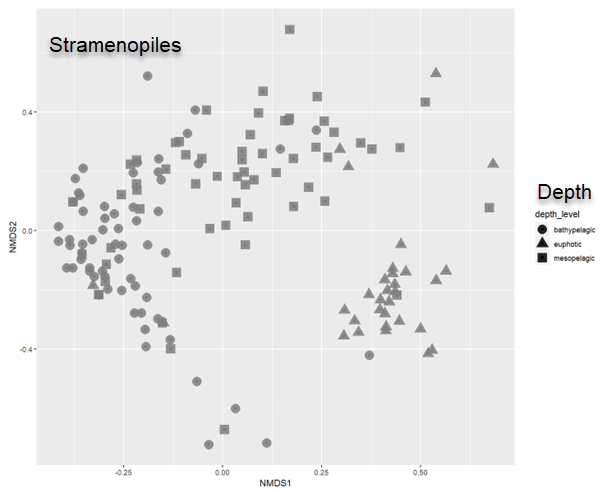
- NMDS: Non-Metric Multidimensional Scaling
Diversity
Beta diversity - Effect of depth on Stramenopiles communities
Intro to metabarcoding