Formation - Cultures des Microalgues
Daniel Vaulot
2023-09-20
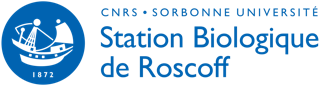

Information management
Outline
- Strain information: metadata
- Keeping track of the metadata: database
- Displaying the data: web site
- Analyzing the data
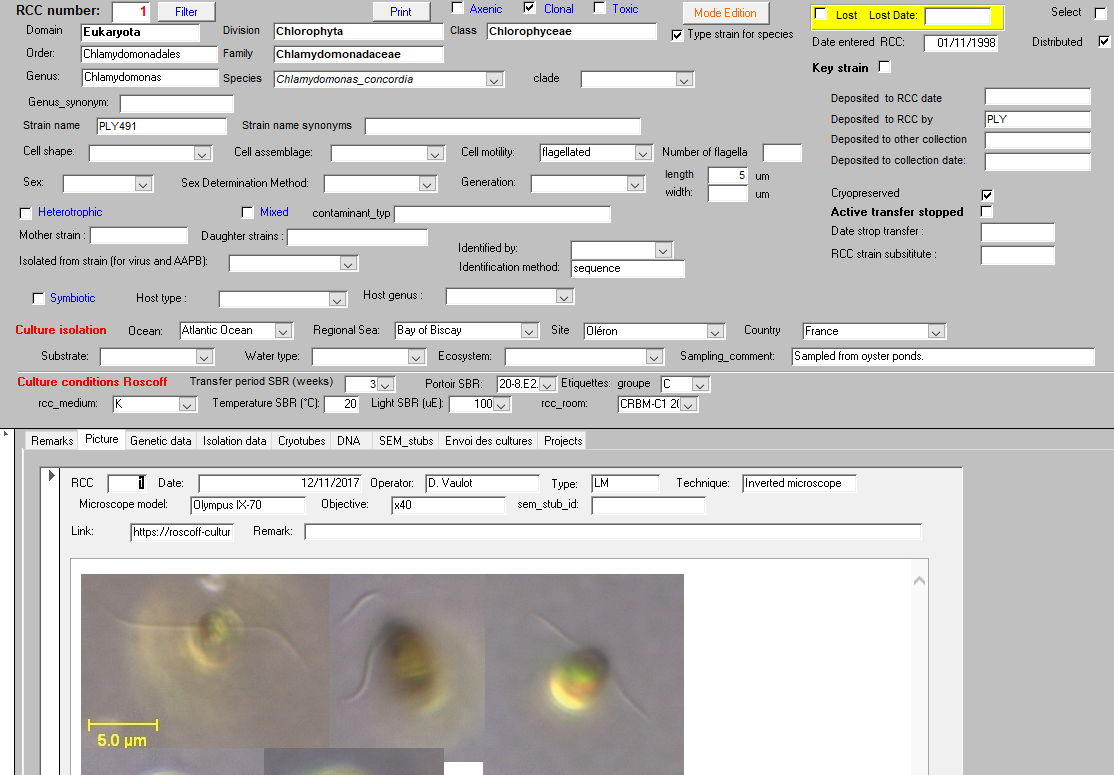
Metadata
What are metadata ?
Metadata are data related to each strain.
They are used to determine the ID-card of the strain.
- Unique identifier
- Strain name
- Taxonomy
- Origin
- Status of strain
- Images
- Maintenance conditions
- ABS status
- Sequences
- Publications
Strain identification
- Unique identifier (RCC1, RCC2…)
- This number is fixed and should be always used
- It is given only for stable cultures
- Strain name
- This is given during the isolation process
- It contains reference to cruise or project
- Important to provide synomyms if they exists
- Taxonomy
- Follow standard (Algaebase)
- Be consistent
- Can be in separate table (see later)
- RCC use 7 levels
- Domain
- Division
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
- Identification can be at higher level only (e.g. class)

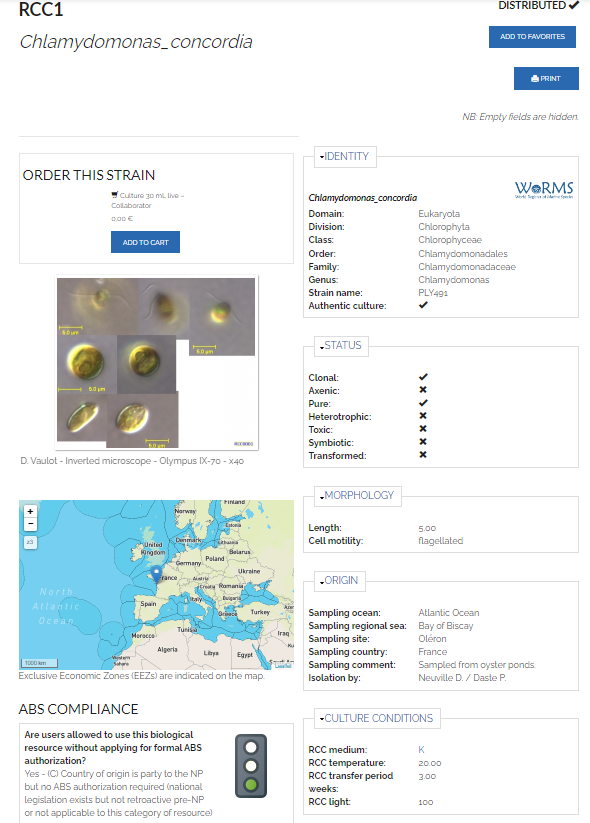
Strain status
- Alive ?
- Never erase information about a strain even if it has been lost.
- Lost: Yes/no
- Date of loss
- Distributed ?
- Strains may be kept private untill described
- Clonal ?
- Arise from single cells
- Mixed ?
- With heterotroph ?
- ABS status (Nagoya convention)
- See Ian presentation
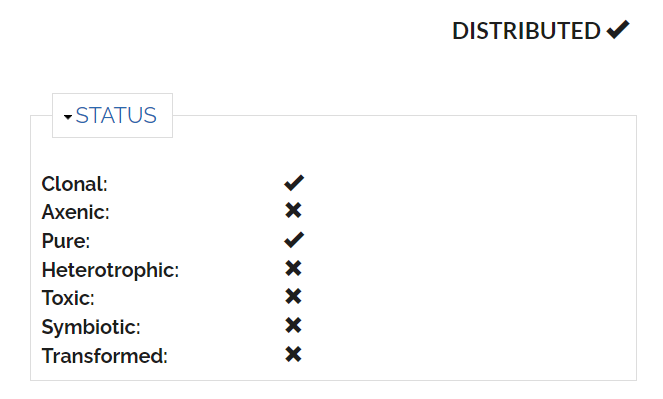
Strain isolation
- Sampling
- Date (see ABS)
- Position
- Depth
- Ocean / Regional Sea
- Site
- Country (see ABS)
- Substrate (water, sediment)
- Temperature / Salinity
- Isolation
- Method
- Medium
- Temperature
- Light
Phenotype
- Life mode
- Phototrophic / Heterotrophic
- Symbiotic
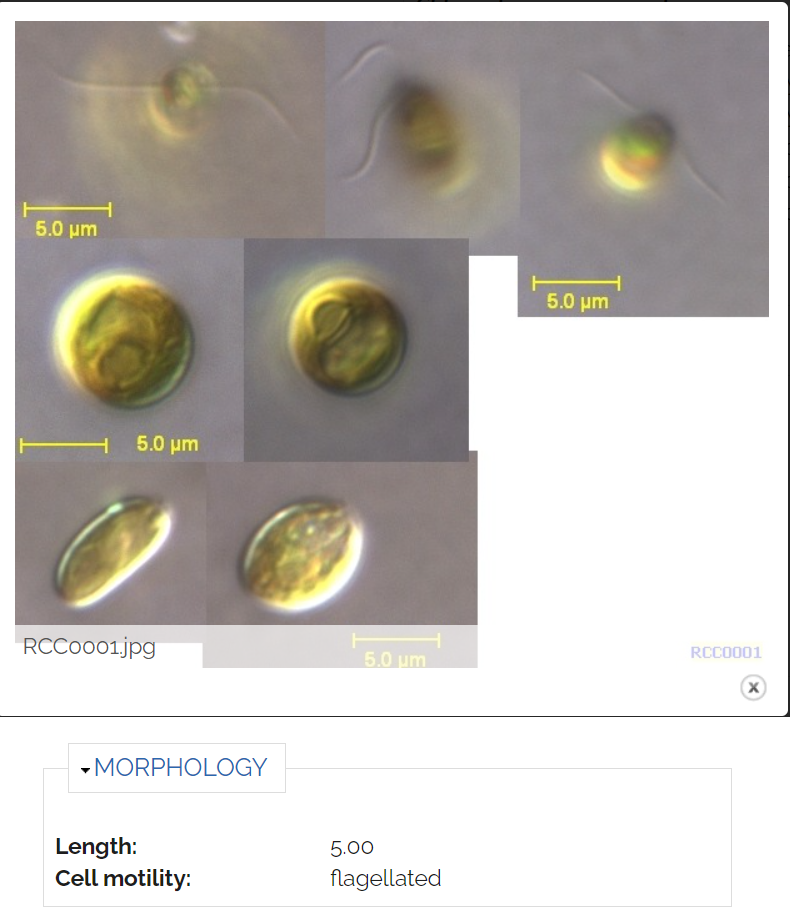
- Morphology
- Cell size
- Cell shape
- Motility
- Colonial ?
- Images
Other information
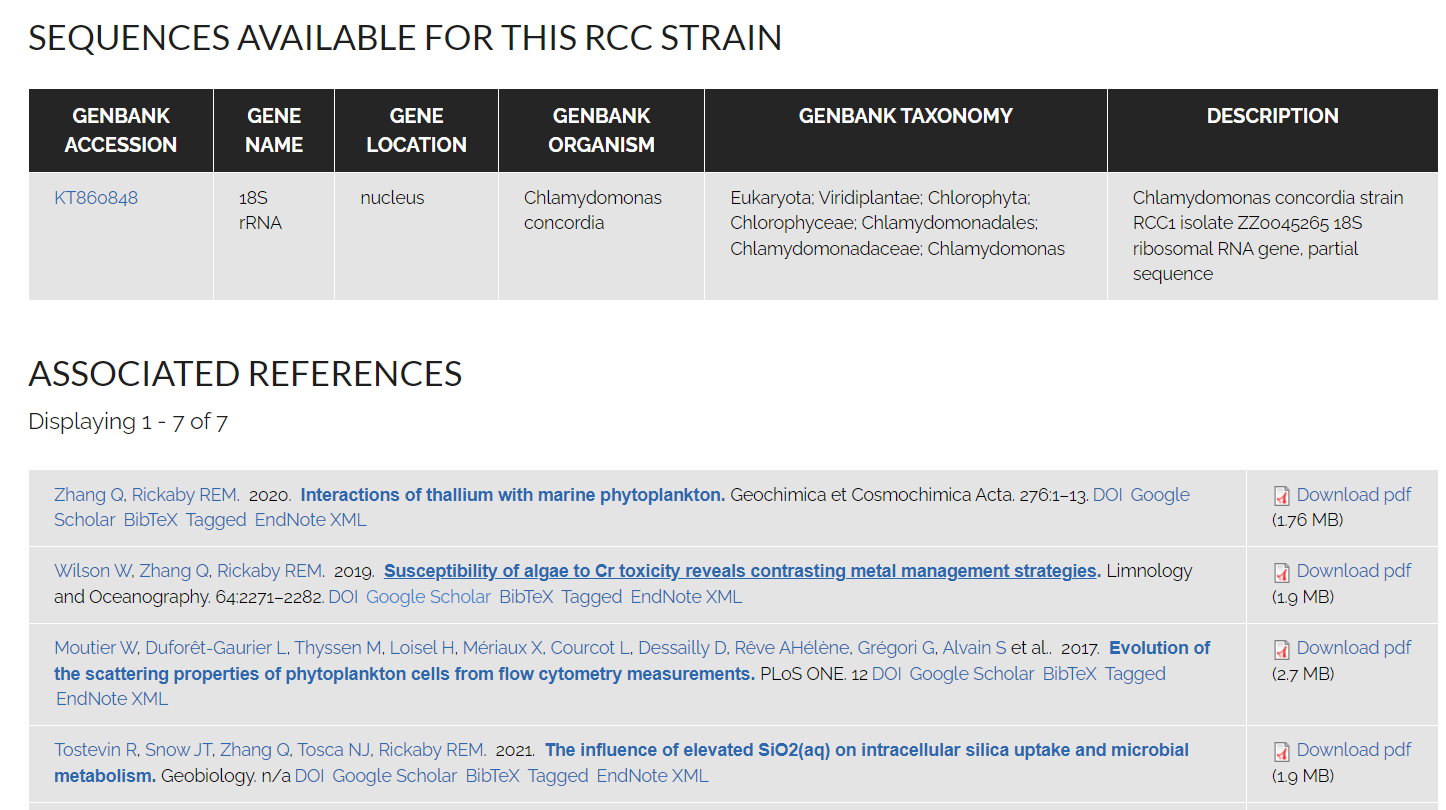
- Genetic sequences
- Pigment composition
- References for the strain
Management
- Culture localisation
- Media batches
- Cryoconservation
- DNA
- Distribution
Databases
How to keep track of the information ?
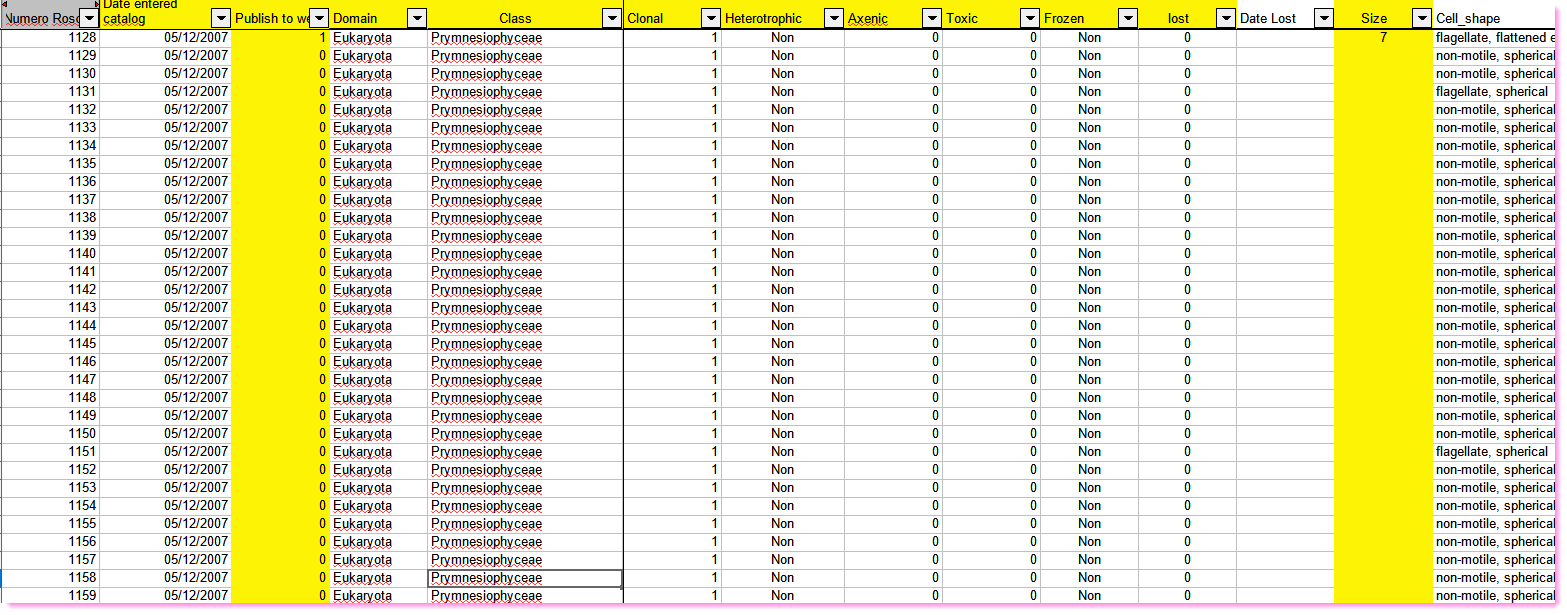
Excel worksheet
Advantages
- Everyone can use Excel
Disadvantages
- Difficult to share
- No rule enforcement for each field
- Too many formatting
Google worksheet
Advantages
- More easy to share
- Can trace who modifies
Disadvantages
- Same as Excel
How to keep track of the information ?
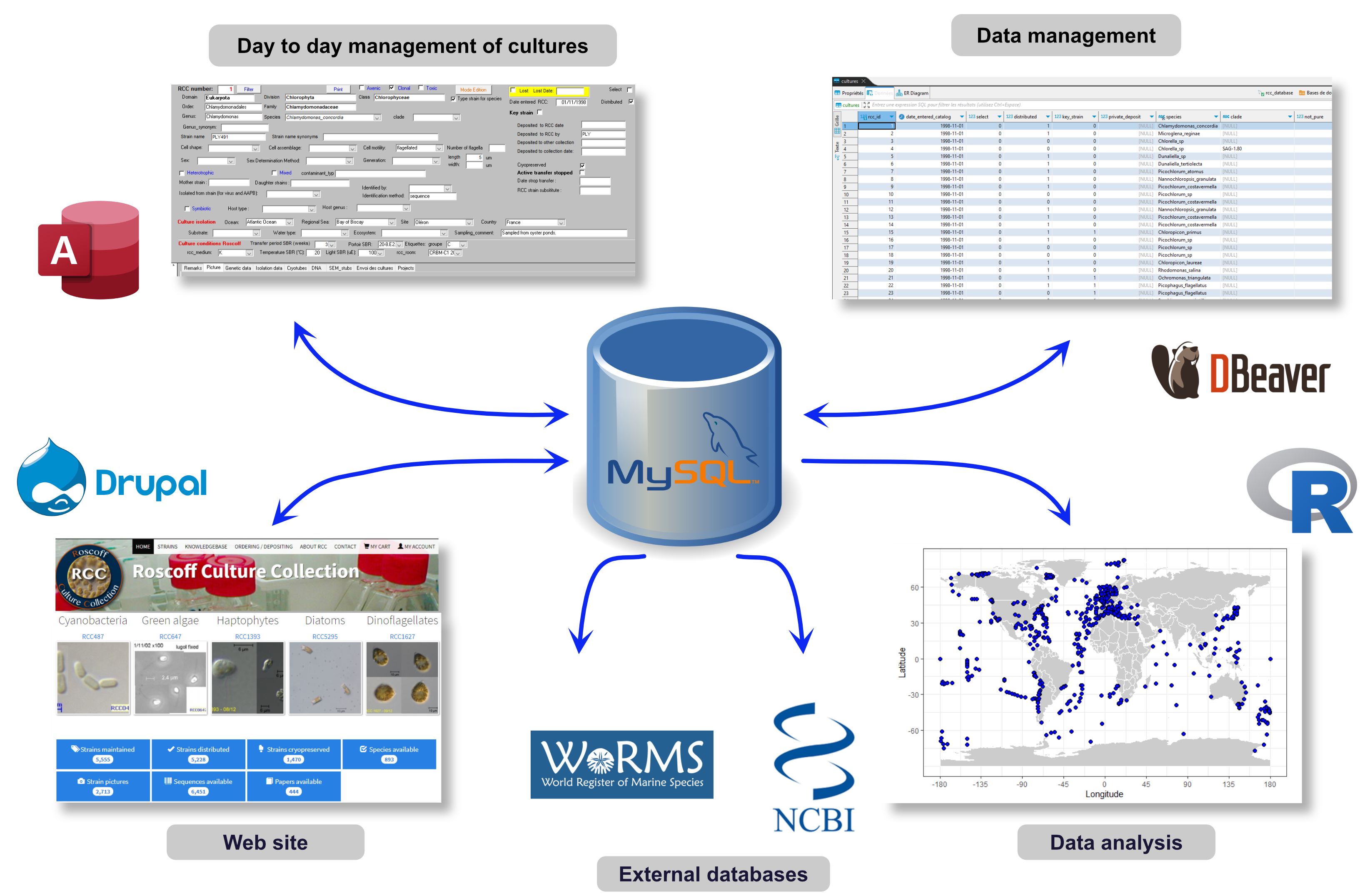
SQL relational databases
Advantages
- Allow to structure information much better
- Relationships between different tables
- Many choices for implementation:
- local (SQlite or Access)
- remote on the cloud (MySQL)
Disadvantages
- Requires using specific tools
- Need computer skills
How to keep track of the information ?
Web based solutions
Advantages
- Single interface
- No computer skills needed
Disadvantages
- Complex implementation
- No out-of-the-box software
- Subcontract to company (e.g. SCROL)
- Slower for some management tasks
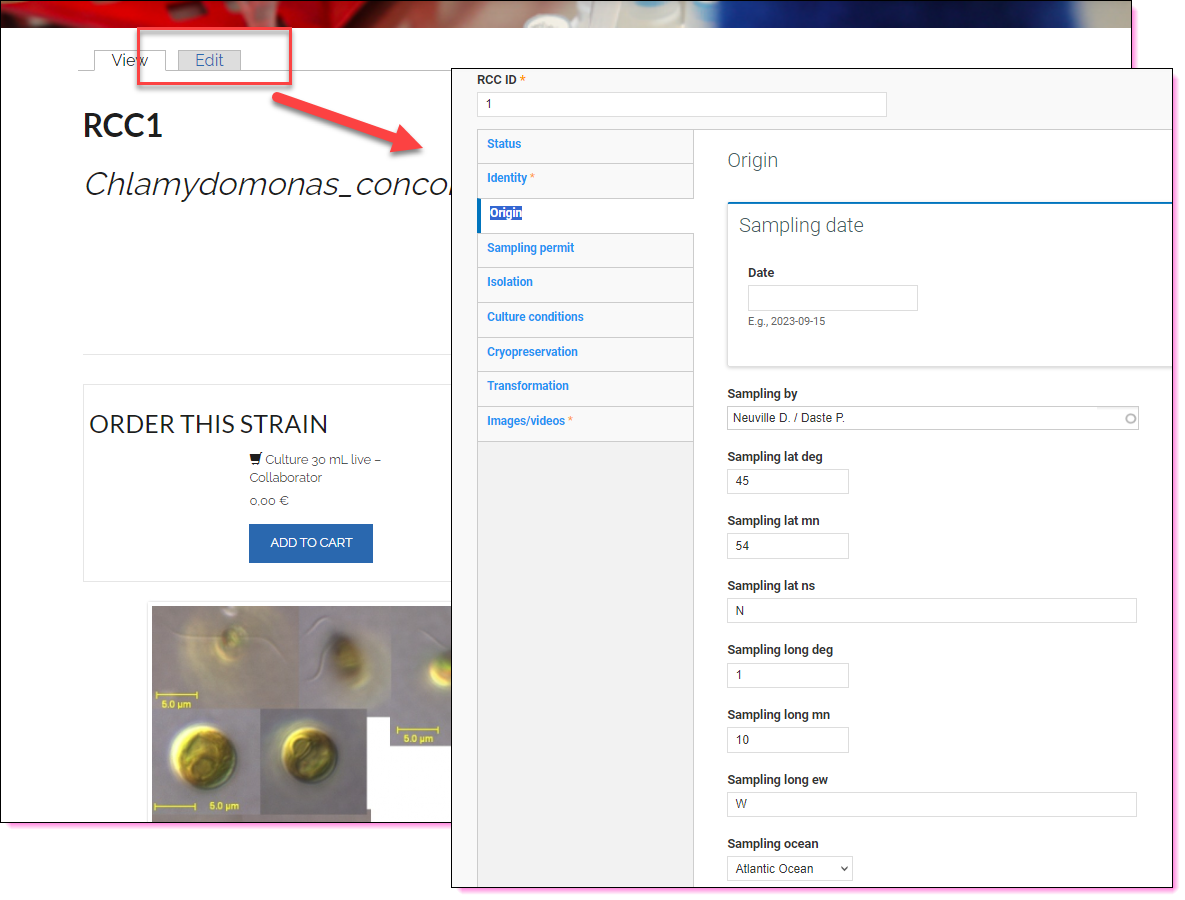
The Roscoff Culture Collection solution
This solution has been elaborated over 20 years with many iterations…
- Start from a database
- Initially Microsoft Access
- Since 2017 MySQL
- Link to web site (3 generations)
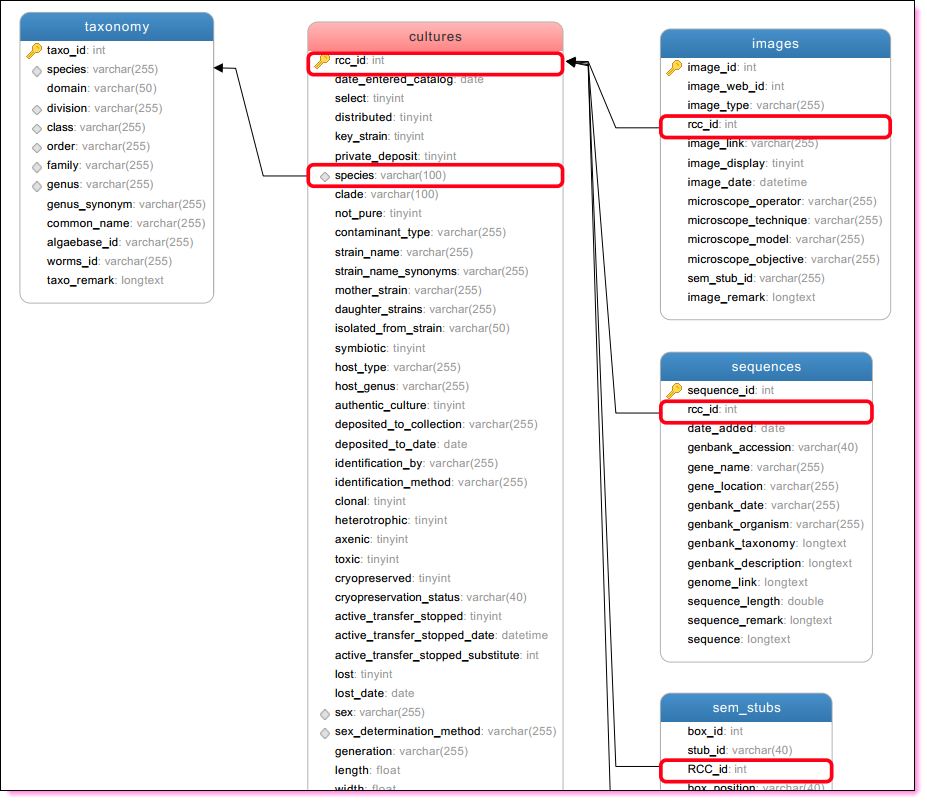
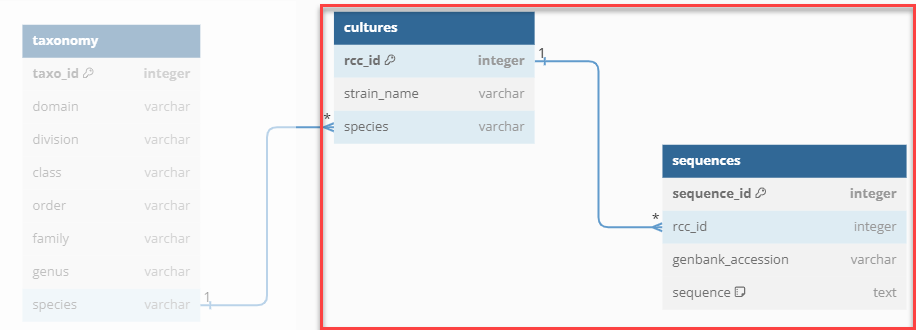
The RCC MySQL scheme
30 Tables

- cultures
- taxonomy
- images
- sequences
- ABS information
- samples (DNA, SEM filters)
- media (seawater etc…)
- transfer groups
- cryopreservation
- orders
- list of predefined values
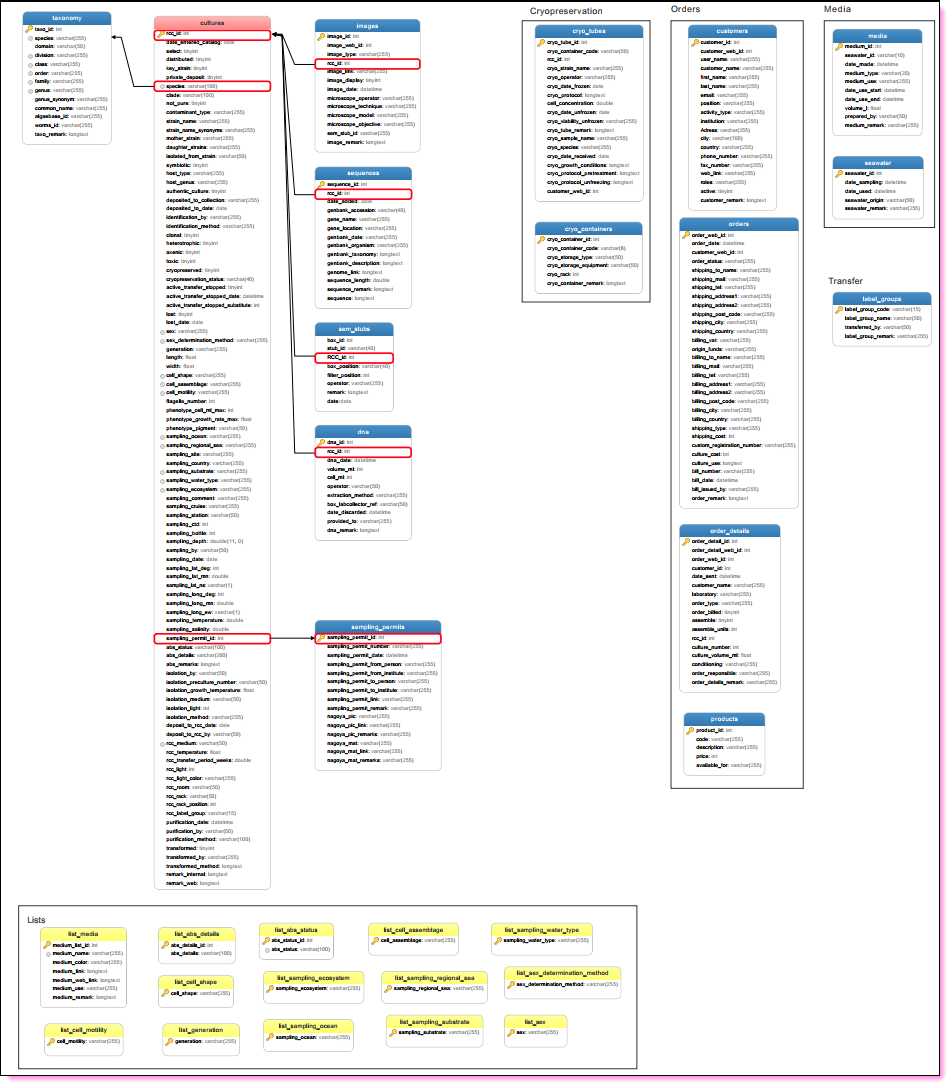
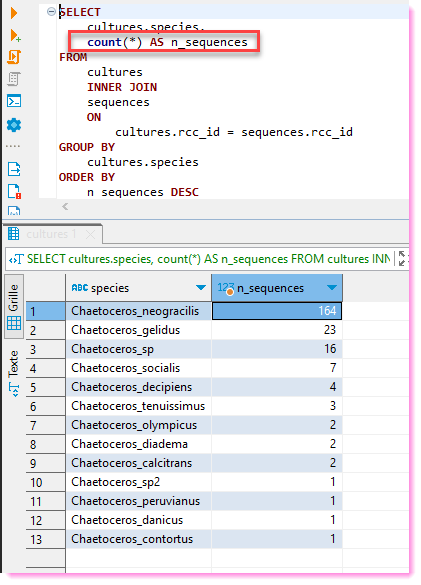
A simple MySQL scheme with 3 tables
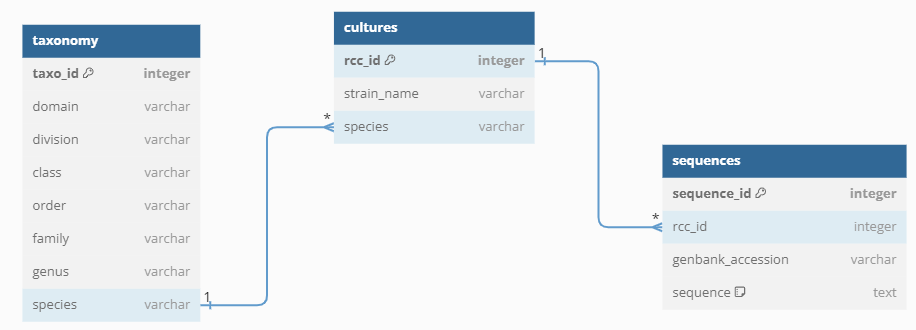
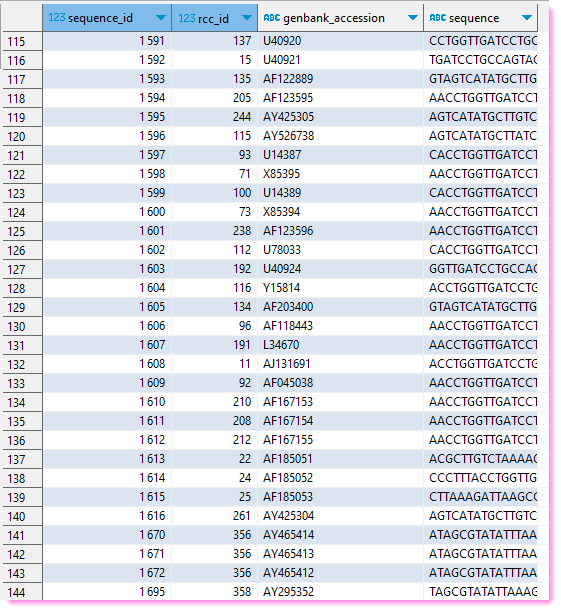
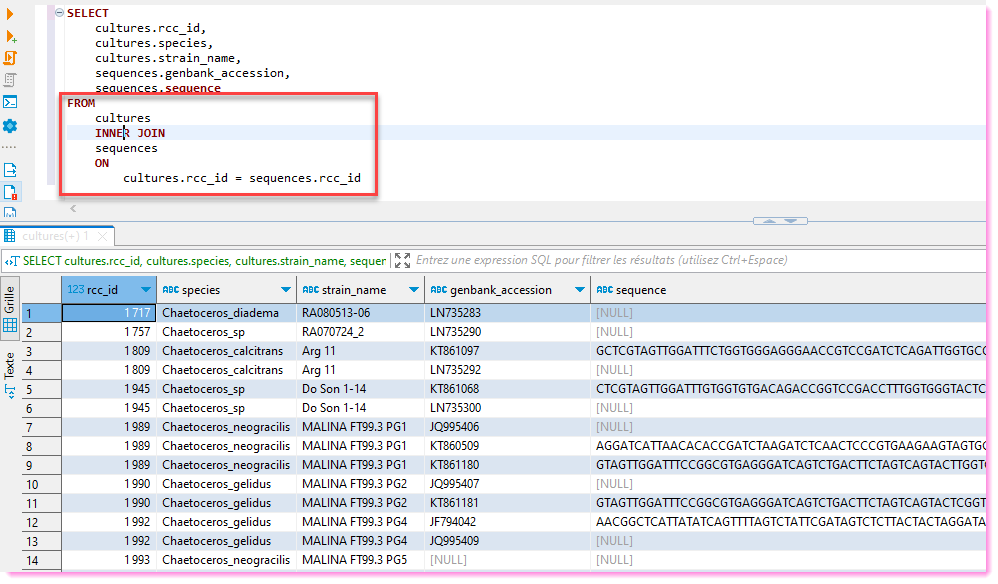
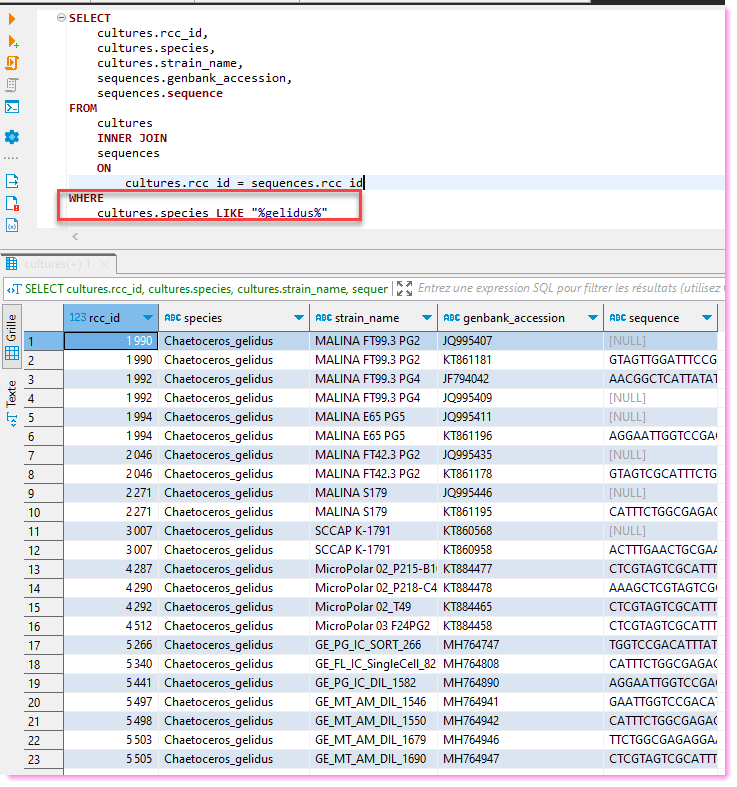
Joining information between 2 tables
Most compelling reason to use SQL databases.
Impossible to do with Excel
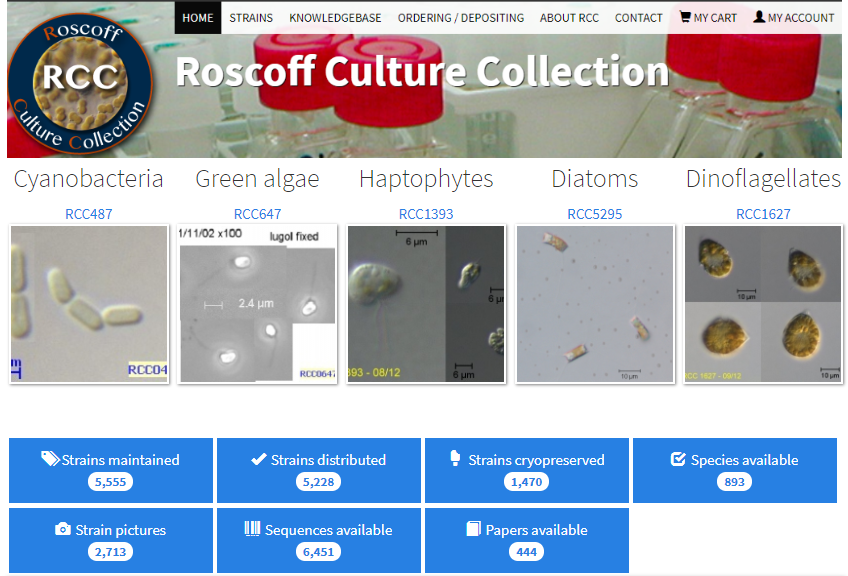
Website
Website
- Strain information
- Flexible search
- Taxonomy
- Strain name
- Localisation
- Information on:
- Culture
- Media composition
- Cryopreservation
- Ordering
- User registration
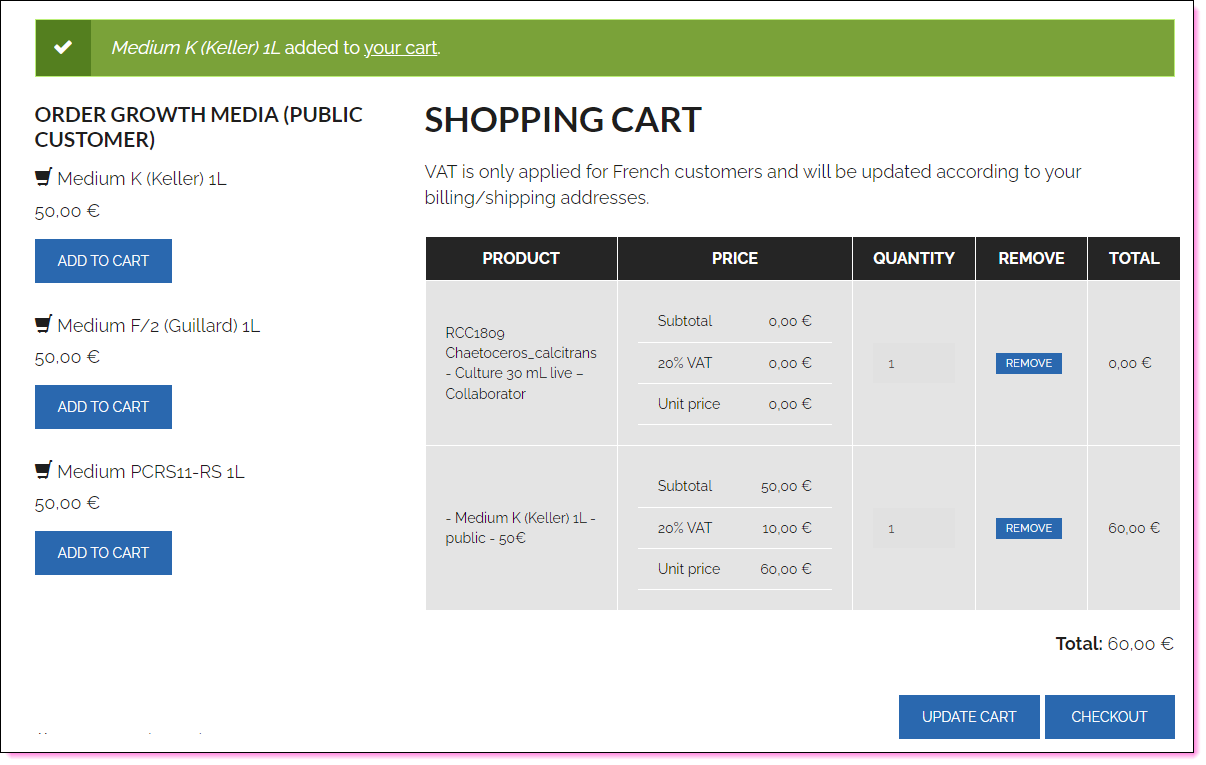
- Strain selection
- Payment
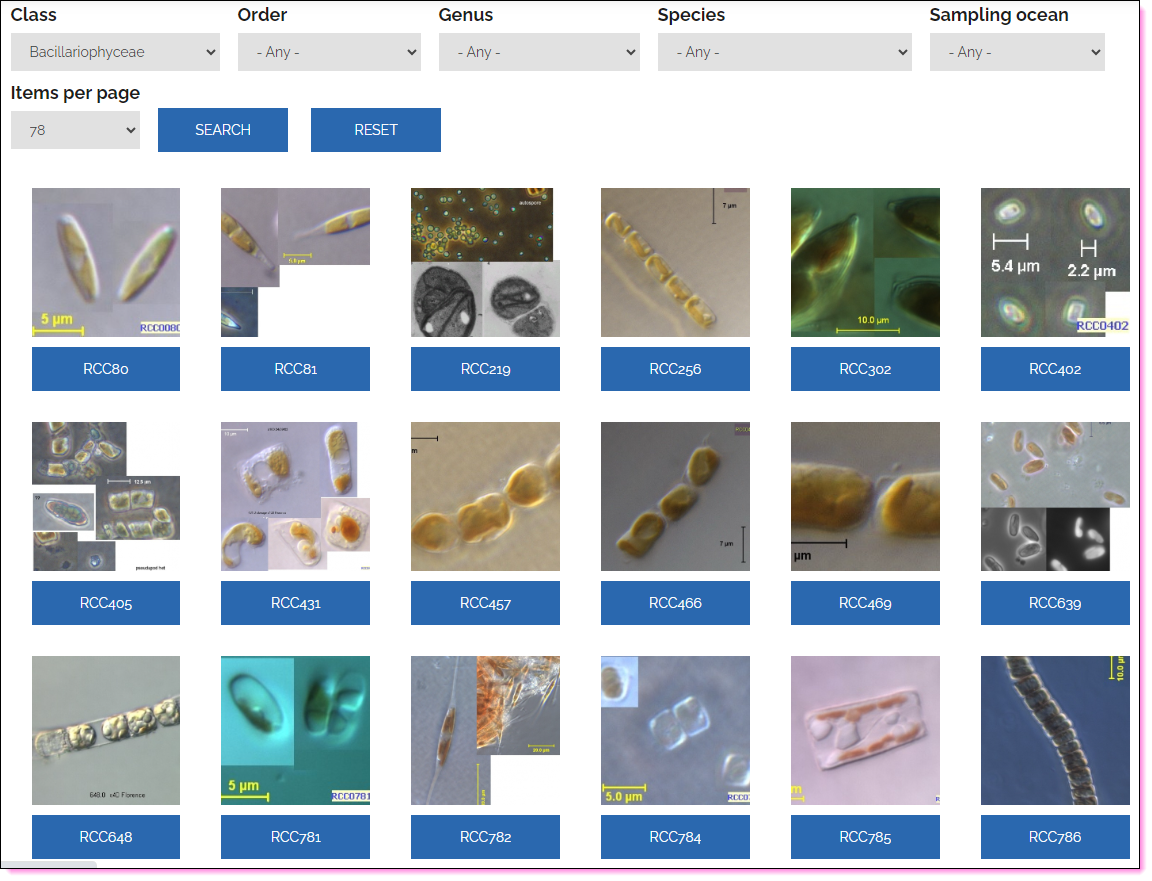
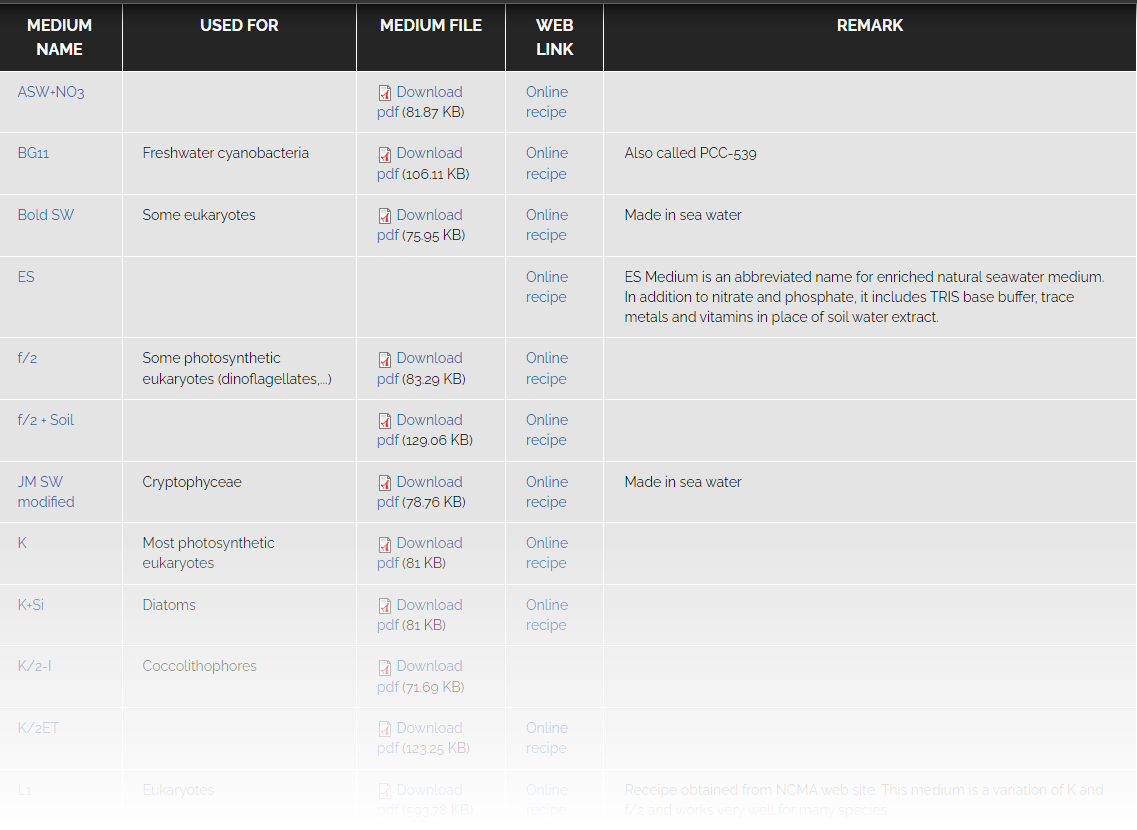
Strain information


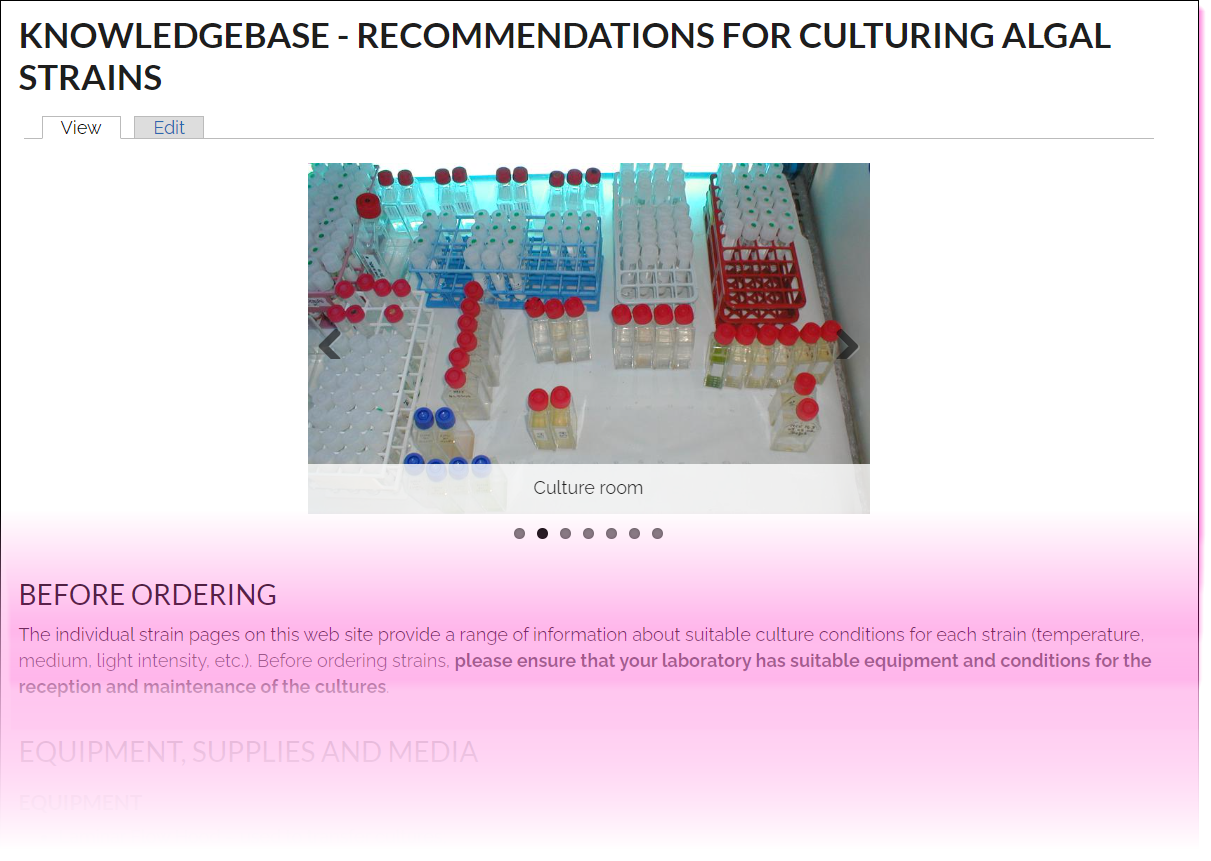
Knowledgebase

Order
Web site types
Static
- Data are updated at intervals
- Update by uploading text file
- Fine for strain listing etc…
- Cannot be used for ordering
- Easy to setup
- Many solutions
- Wordpress
- Google sites
- R and Netifly

Dynamic
- Data are updated in real time
- Link to database
- Can be used to set up a “shop”
- Many solutions
- Web builder
- CMS such as Drupal (cf. SCROL)

Analysis of data
Analysis
- Necessary to follow your collection
- Can use Excel
- Better use a programming language
- R
- Python
Examples
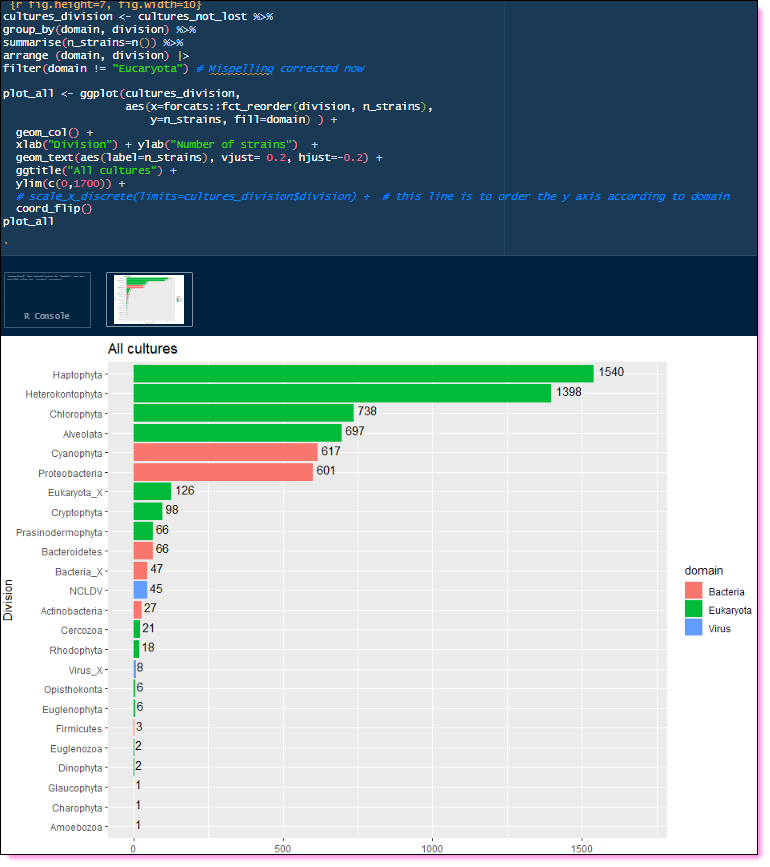
Class composition
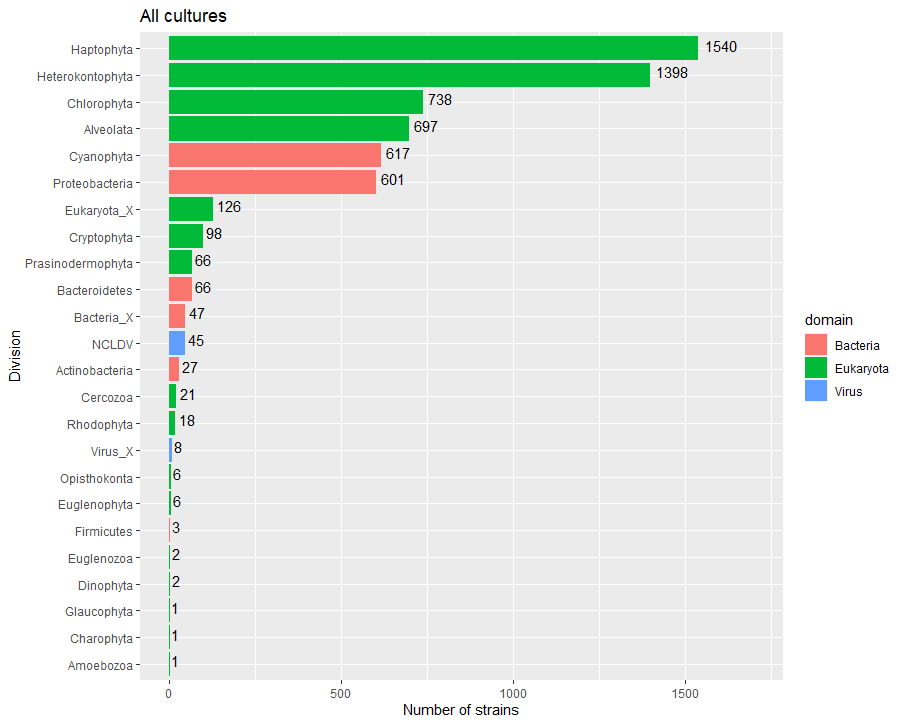
Major species
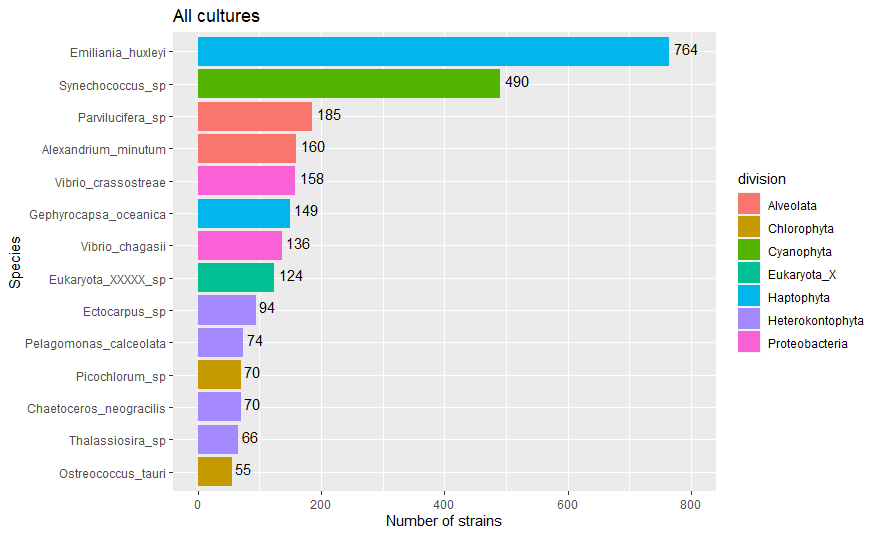
Localisation
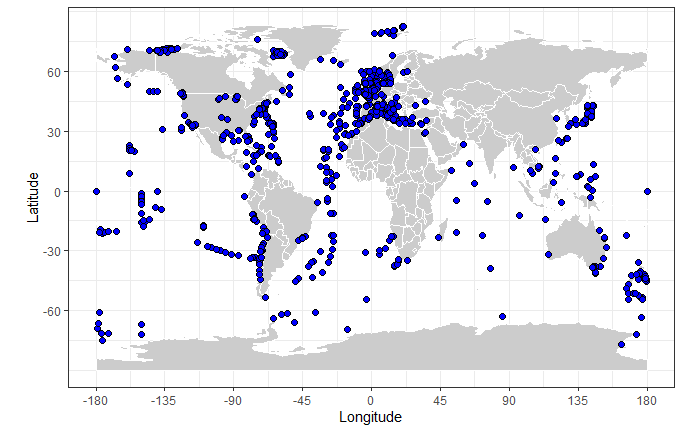
Collection history
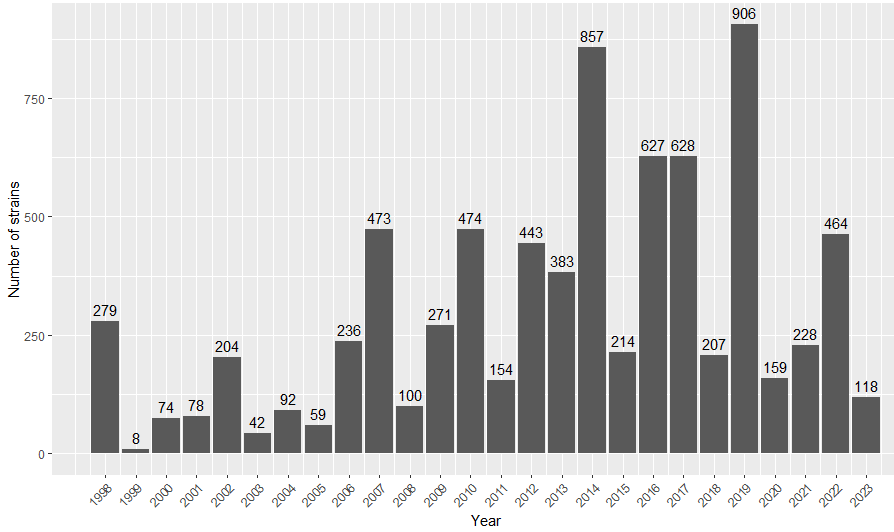
Cryopreservation

Orders
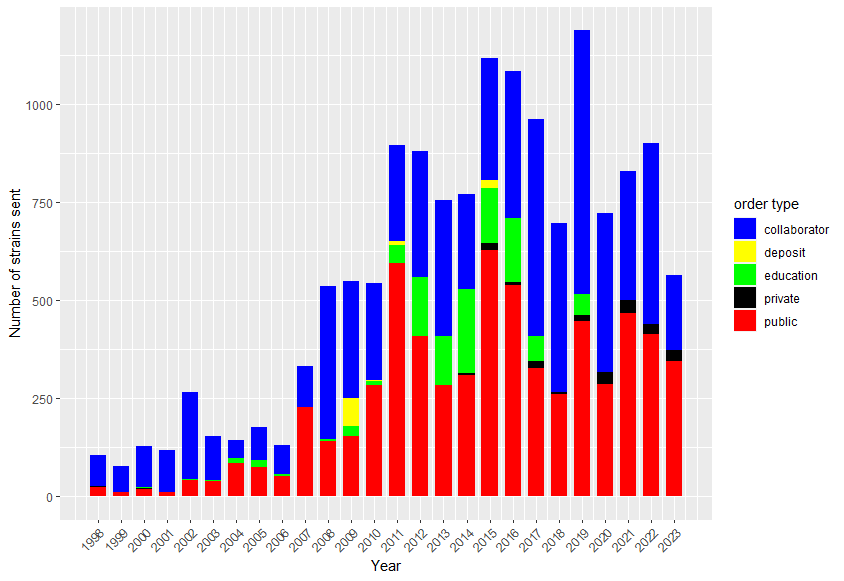
Important points
- Unique numeric identifier for each strain
- Never delete information (e.g. lost strains)
- Many solutions to keep track
- Use of SQL database is recommended
- Start with small website
- Collection analysis helps management